The distributor pickup coil generates the G2 signal, which, along with the CKP sensor signal, helps the fuel injection computer control ignition timing and activate the igniter, ignition coil, and fuel injectors.
Over time, the distributor pickup coil will eventually fail. When it does, the engine won't start.
In this tutorial, I'll show you the two simple tests that'll help you determine whether the pickup coil is still functioning or has failed.
Contents of this tutorial:
- What Does The Distributor Pickup Coil Do?
- Symptoms Of A Bad Pickup Coil.
- Distributor Connector Circuit Descriptions.
- Where To Buy The Distributor Pickup Coil.
- TEST 1: Checking The Pickup Coil's Resistance With A Multimeter.
- TEST 2: Testing The Pickup Coil's Output With A Multimeter.
- More 1.6L Toyota Corolla Tutorials.
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 1.6L (4A-FE) Toyota Corolla: 1996, 1997.
Ignition System Diagnostic Tests:
- How To Test The Ignition Coil (1996-1997 1.6L Toyota Corolla).
- How To Test The Igniter (1996-1997 1.6L Toyota Corolla).
- How To Test The CKP Sensor (1996-1997 1.6L Toyota Corolla).
Ignition System Wiring Diagram:
Engine No-Start Diagnostics:
What Does The Distributor Pickup Coil Do?
Here's what you need to know about the pickup coil before we dive into testing:
- Purpose of the pickup coil: In the 1996-1997 1.6L Corolla, the distributor pickup coil contains a single magnetic sensor that generates the G2 AC voltage signal used for ignition spark control and ignition timing.
- The G2 signal: This signal tells the fuel injection computer when a cylinder is reaching top dead center (TDC), allowing precise control of ignition timing.
- How the G2 signal is generated: As the engine cranks or runs, a reluctor wheel (toothed wheel attached to the distributor shaft) rotates past the magnetic sensor, inducing the AC voltage signal.
- Role in ignition timing: The fuel injection computer reads the G2 signal to determine the exact moment to fire the ignition coil through the igniter (ignition control module). The ignition coil then generates a high-voltage spark, which travels through the distributor cap, rotor, and spark plug wires to the correct spark plug.
Symptoms Of A Bad Pickup Coil
If the pickup coil's bad, your engine might struggle to start or suddenly shut off while running. The two most common signs are:
- Engine won't start:
- The igniter doesn't receive its IGT activation signal.
- The ignition coil doesn't get triggered by the igniter.
- The fuel injectors don't get activated by the fuel injection computer.
- The fuel pump stays off because the fuel injection computer doesn't turn it on.
- Rough running or sudden stalling:
- The engine may misfire, run unevenly, or cut off out of nowhere while you're driving.
- CMP sensor diagnostic trouble code (DTC):
- P0340: Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor Circuit Problem.
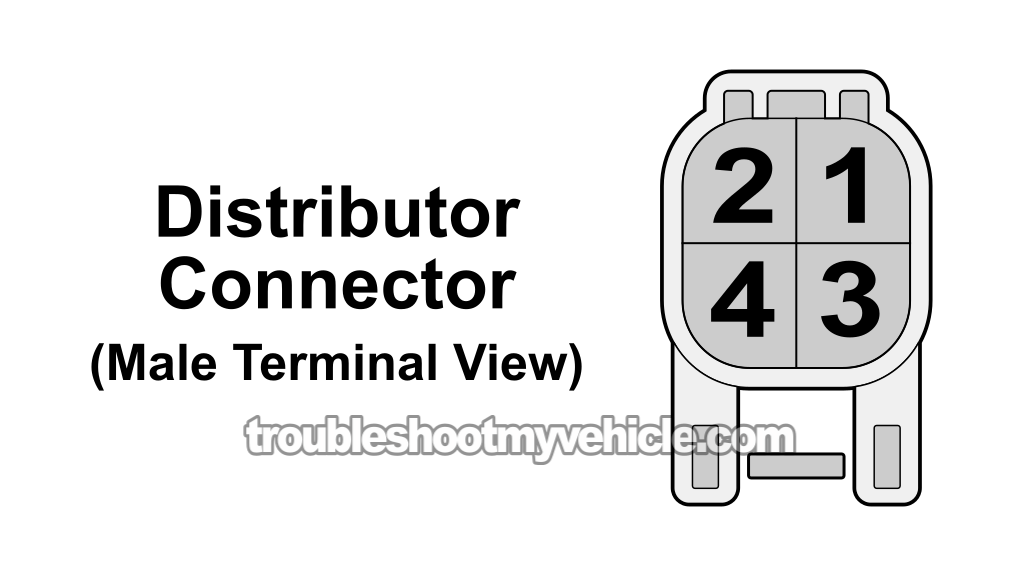
Distributor Connector Circuit Descriptions

Your 1996-1997 1.6L Toyota Corolla's distributor has a 4-wire connector. The connector coming out of the distributor itself has male spade terminals. The engine wiring harness connector has female terminals.
NOTE: The wire colors in the tables below match the engine wiring harness connectors, not the ones directly on the distributor.
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | White (WHT) | NE- → Sensor Ground For G2 |
| 2 | Black (BLK) | G2 → Camshaft Position Signal |
| 3 | Black (BLK) | B+ → Ignition 12 Volts |
| 4 | Black (BLK) | +B2 → Ignition Coil Activation Signal |
Where To Buy The Distributor Pickup Coil
The pickup coil isn't sold separately from the distributor, so if your test results indicate it's bad, you'll need to buy the entire distributor.
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
NOTE: Not sure if the distributor fits your particular Corolla? Don't worry. Once you get to the site, they'll ask you for the specifics of your vehicle. If it doesn't fit, they'll find you the right one.
TEST 1: Checking The Pickup Coil's Resistance With A Multimeter

The most common type of failure that the distributor pickup coil (G2 sensor) will suffer is an internal short-circuit or open-circuit problem.
To see if the G2 sensor's got an internal electrical problem, grab a multimeter, switch it to Ohms (Ω) mode, and check its resistance. If it's within spec, the sensor's likely fine.
If the NE circuit's working properly —meaning no shorts or open-circuits inside— your multimeter should read:
- G2 Sensor: Between 185 and 265 Ohms (engine cold).
NOTE: Do these resistance checks at the distributor's 4-wire connector—the one right on the distributor with male spade terminals.
Let's get started:
- 1
Disconnect the distributor's 4-wire connector from the engine wiring harness.
- 2
Set your multimeter to Ohms mode.
- 3
Measure the resistance between terminals 1 and 2 on the pickup coil connector.
These terminals connect to the G2 sensor. - 4
Your multimeter should read between 185 and 265 Ohms.
Let's interpret your test results:
CASE 1: G2 sensor resistance falls within the correct range. This means the pickup coil doesn't have an internal electrical problem.
You don't have to, but if you wanna be extra sure the pickup coil is working, you can check if it's actually producing a signal in TEST 2: TEST 2: Testing The Pickup Coil's Output With A Multimeter.
CASE 2: G2 sensor resistance is out of range. That confirms the pickup coil's faulty and needs replacing.
Since you can't buy the pickup coil assembly separately, the whole distributor's gotta be replaced.
If you wanna double-check that the G2 sensor is bad, perform TEST 2: TEST 2: Testing The Pickup Coil's Output With A Multimeter.
TEST 2: Testing The Pickup Coil's Output With A Multimeter

When the engine cranks, the G2 sensor generates an AC voltage. This AC voltage can easily be confirmed with a multimeter set to Volts AC mode.
This is what to look for:
- Good G2 sensor: The multimeter should read between 0.4 and 1.2 Volts AC as the engine cranks.
- Bad G2 sensor: The multimeter will show 0 Volts AC while cranking the engine.
NOTE: The G2 sensor's AC voltage output depends on how fast the engine turns over, which is directly tied to the battery's charge. To get the best results, make sure your Corolla's battery is fully charged before starting this test. If the battery's weak or dead, charge it up first.
Alright, let's dive in:
- 1
Disconnect the distributor's 4-wire connector from the engine wiring harness.
- 2
Switch your multimeter to Volts AC mode.
- 3
Probe male spade terminals 1 and 2 on the 4-wire distributor connector using your multimeter's test leads.
Terminals 1 and 2 connect to the G2 sensor.
NOTE: Make sure you're testing the male spade terminals on the distributor's connector, not the female ones on the engine wiring harness connector. - 4
Have your helper crank the engine while you watch the multimeter.
CAUTION: Stay alert while the engine's cranking. - 5
Your multimeter should read an AC voltage fluctuating between 0.4 and 1.2 Volts AC.
Now, let's go over your test results:
CASE 1: The multimeter shows the expected AC voltage. That means the G2 sensor's working fine.
CASE 2: The multimeter reads 0 AC voltage. This confirms the pickup coil assembly's faulty and needs replacing.
More 1.6L Toyota Corolla Tutorials
You can find a complete list of 1.6L Toyota Corolla tutorials and wiring diagrams in this index:
Here's a sample of the tutorials you'll find there:
- How To Test The Throttle Position Sensor (1989-1997 1.6L Toyota Corolla).
- How To Test Engine Compression (1989-1997 1.6L Toyota Corolla).
- How To Test The Fuel Injectors (1993-1997 1.6L Toyota Corolla).
- How To Do A Cylinder Balance Test (1989-1997 1.6L Toyota Corolla).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!



