TEST 5: Making Sure The Coil Pack Is Getting 12 Volts
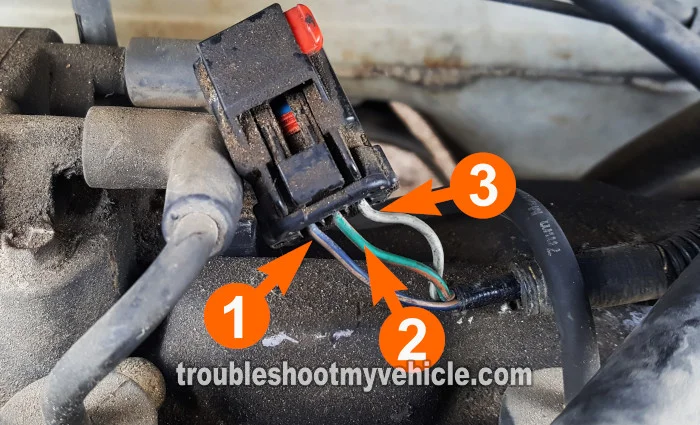
In this test section, we're gonna make sure that the ignition coil pack is getting 10 to 12 Volts when the engine is being cranked.
The wire that feeds these 10 to 12 Volts to the ignition coil pack is the wire labeled with the number 2 in the photo above.
We'll use a multimeter to check for these 10 to 12 Volts. These are the test steps:
NOTE: Depending on the year of your particular minivan, the colors of the wires may not match those in the photo above. Don't worry, the circuits are the same. The wire labeled with the number 2 is the one that supplies power to the ignition coil pack.
- 1
Disconnect the ignition coil pack from its connector.
- 2
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 3
Probe the circuit labeled with the number 2 (see photo above) with the red multimeter test lead (using an appropriate tool).
You have the option of testing the front of the female terminal (of the connector). Just be careful that the multimeter probe doesn't damage the female terminal, or you'll have to get a new connector.
NOTE: The three wires in the ignition coil pack's connector are usually sheathed in black electrical tape that has probably turned plastic hard, remove enough of this electrical tape to expose the three wires for testing. - 4
Connect the black multimeter test lead to the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 5
Have your helper crank the engine.
NOTE: This voltage must be checked with the engine cranking. - 6
You should see 10 to 12 Volts on your multimeter.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The multimeter registered 10 to 12 Volts DC. This is the correct and expected test result.
The next step is verify that the activation signals are present, go to: TEST 8: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Pack Is Getting Its Activation Signals.
CASE 2: The multimeter DID NOT register 10 to 12 Volts DC. Re-check all of your connections and retest. If still no voltage is present, this result exonerates the ignition coil pack since without it the ignition coil pack will not function.
Repairing the cause of this missing voltage will solve the 'no-spark no-start' issue of your minivan.
The most common cause of this missing voltage is a bad crankshaft position sensor. You can find a step-by-step test of the crankshaft position sensor here: Testing The Crankshaft Position Sensor (1996-2002 2.4L Caravan, Grand Caravan, Voyager, Grand Voyager).
TEST 6: Checking The Activation Signal For Cylinders 1 And 4

The individual ignition coil (inside the coil pack) that supplies spark to cylinders #1 and #4 only does so when it receives an activation signal from the fuel injection computer.
You and I can easily check for the presence of this activation signal (when the engine is cranking) with a simple LED light.
If you don't have an LED light, you can find out more about it and where to buy one here: The LED Light Test Tool And How To Make One (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
NOTE: Depending on the year of your particular minivan, the colors of the wires may not match those in the photo above. Don't worry, the circuits are the same. The wire labeled with the number 3 is the one that supplies the ignition coil pack activation signal for cylinders #1 and #4.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Disconnect the ignition coil pack from its connector.
- 2
With an appropriate tool, connect the black lead of the LED light to the wire identified with the number 3 in the photo above.
This is the circuit that feeds the activation signal to the ignition coil (within the coil pack) that feeds spark to cylinders 1 and 4 simultaneously.
NOTE: You can also insert the end of the black LED wire into the female terminal of the wire. Just be careful that the wire doesn't damage the female terminal, or you'll have to get a new connector. - 3
Connect the red lead of the LED light to the battery positive (+) terminal with a long jumper cable.
NOTE: You can also insert the end of the red LED wire into middle female terminal of the connector (which will have 10 to 12 Volts with the engine cranking). Just be careful that the wire doesn't damage the female terminal, or you'll have to get a new connector. - 4
Have your helper crank the engine while you observe the LED light.
- 5
If the activation signal is present, the LED light will flash ON and OFF the whole time the engine was cranking.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The LED light flashed ON and OFF the whole time the engine was cranking. This is the correct test result and it confirms that the fuel injection computer (PCM) is providing the activation signal and the circuit is OK.
This result confirms that the ignition coil pack is bad and needs to be replaced only if you have:
- Confirmed that the spark plug wires for cylinder #1 and cylinder #4 are not sparking (TEST 1).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil pack towers for cylinder #1 and cylinder #4 are not sparking (TEST 3).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil's activation signal is present in this test section.
CASE 2: The LED light DID NOT flash ON and OFF the whole time the engine was cranking. Without an activation signal, the ignition coil pack will not fire off spark to cylinders #1 and #4.
The most likely cause of this missing signal is either an open-circuit problem in the wire between the connector and the PCM or the PCM is fried (altho a fried PCM is rare). With this result you have eliminated the coil pack as the source of the misfire condition or no-spark condition.
TEST 7: Checking The Activation Signal For Cylinders 2 And 3

Testing for the activation signal is a very simple and straightforward process.
To check for the activation signal for cylinders #2 and #3, we're gonna' use an LED Light. If you don't have one, you can find out more about it and where to buy one here: The LED Light Test Tool And How To Make One (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
NOTE: Depending on the year of your particular minivan, the colors of the wires may not match those in the photo above. Don't worry, the circuits are the same. The wire labeled with the number 1 is the one that supplies the ignition coil pack activation signal for cylinders #2 and #3.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Disconnect the ignition coil pack from its connector.
- 2
With an appropriate tool, connect the black lead of the LED light to the wire identified with the number 1 in the photo above.
This is the circuit that feeds the activation signal to the ignition coil (within the coil pack) that feeds spark to cylinders 2 and 3 simultaneously.
NOTE: You can also insert the end of the black LED wire into the female terminal of the wire. Just be careful that the wire doesn't damage the female terminal, or you'll have to get a new connector. - 3
Connect the red lead of the LED light to the battery positive (+) terminal with a long jumper cable.
NOTE: You can also insert the end of the red LED wire into middle female terminal of the connector (which will have 10 to 12 Volts with the engine cranking). Just be careful that the wire doesn't damage the female terminal, or you'll have to get a new connector. - 4
Have your helper crank the engine while you observe the LED light.
- 5
If the activation signal is present, the LED light will flash ON and OFF the whole time the engine was cranking.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The LED light flashed ON and OFF the whole time the engine was cranking. This is the correct test result and it confirms that the fuel injection computer (PCM) is providing the activation signal and the circuit is OK.
This result confirms that the ignition coil pack is bad and needs to be replaced only if you have:
- Confirmed that the spark plug wires for cylinders #2 and #3 are not sparking (TEST 1).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil pack towers for cylinder #2 and cylinder #2 are not sparking (TEST 3).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil pack's activation signal is present in this test section.
CASE 2: The LED light DID NOT flash ON and OFF the whole time the engine was cranking. Without an activation signal, the ignition coil pack will not fire off spark to cylinders #2 and #3.
The most likely cause of this missing signal is either an open-circuit problem in the wire between the connector and the PCM or the PCM is fried (altho a fried PCM is rare). With this result you have eliminated the ignition coil pack as the source of the misfire condition or no-spark condition.
