TEST 3: Manually Inducing A Lean Air/Fuel Mixture
In this test section, we're going to check the performance of the rear O2 sensor to make sure it's actually telling us the truth about the catalytic converter's health.
We can easily check the performance of the rear O2 sensor by manually inducing a lean air/fuel mixture and then watching how the sensor responds (on the scan tool).
We'll induce a lean air/fuel mixture by partly disconnecting a large vacuum hose from the intake manifold. The vacuum hose I usually disconnect is the one that connects to the power brake booster.
It's important to note that I don't disconnect the hose completely, as this would shut down the engine, I just loosen it enough to let some vacuum escape and get a reaction from the rear O2 on the scan tool.
If you plan on partly disconnecting the power brake booster's vacuum supply hose, prep for the test by first disconnecting and then reconnecting the hose from its vacuum port on the intake manifold before you start the engine. Why? Because the hose tends to stick to its vacuum port (on the intake manifold), so doing this prep step makes it easier and safer to slightly disconnect it when the engine is running.
Once we've completed this test, we'll move on to the second O2 sensor performance test which is about creating a rich air/fuel mix and observing the sensor's reaction (we'll tackle this in TEST 4).
CAUTION: While performing this test, the engine will be running. Be extremely careful around any moving parts to avoid injury.
Let's get started:
- 1
Crank and start your minivan's engine. Let the engine idle for about 15 minutes.
- 2
Connect your scan tool to your vehicle's diagnostic port.
- 3
Enter the Live Data function.
- 4
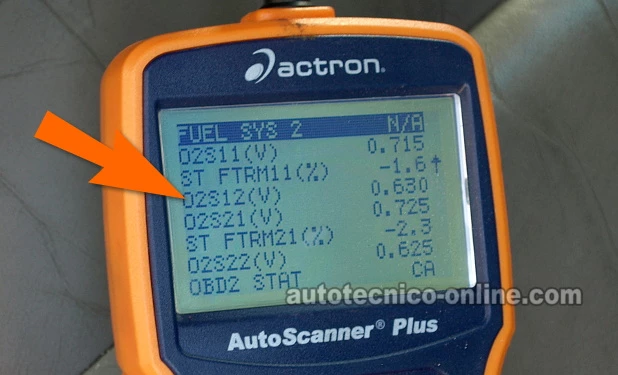
Scroll down to the rear oxygen sensor voltage reading. This reading is generally labeled as O2S12.
The O2S12 reading will show you the voltage activity of the rear oxygen sensor. - 5
After 15 minutes of the engine running, the voltage reading should oscillate between 0.100 and 0.500 Volts every few seconds.
If the reading shows a fixed value (that neither rises nor falls), don't worry. Proceed to the next step. - 6
Disconnect a large vacuum hose with the engine running while watching the O2S12 reading on your scan tool's screen.
NOTE: If the engine shuts off, simply restart it and begin from step 1 (and disconnect the hose only slightly this time). - 7
As you're letting air in (or letting vacuum escape), the O2S12 voltage reading should drop to 0.100 to 0.200 Volts. And while the hose is open or disconnected (and depending on the amount of the vacuum leak), the voltage should stay between 0.100 to 0.200 Volts.
- 8
Shut off the vacuum leak.
- 9
The voltage reading should start to oscillate between 0.100 Volts to 0.500 Volts within a couple of seconds after shutting off the vacuum leak.
Let's take a look at what the test results mean:
CASE 1: The voltage dropped to 0.100 Volts when opening (disconnecting) the vacuum hose. This indicates that the oxygen sensor is working correctly and is not faulty (as it can react to the lean air/fuel mixture and report it).
The next step is to now check that the oxygen sensor can react and report a rich air/fuel mixture. For this test, go to: TEST 4: Manually Inducing A Rich Air/Fuel Mixture.
CASE 2: The voltage did NOT drop to 0.100 Volts when opening (disconnecting) the vacuum hose. This result indicates that the oxygen sensor is faulty and needs to be replaced.
If the rear oxygen sensor were operating correctly, it would have reacted immediately upon disconnecting the hose and generated a voltage of around 0.1 Volts (100 milliVolts). Since it didn't, you can correctly conclude that it's faulty and needs to be replaced.
CASE 3: The wiring of the rear oxygen sensor is burned and stuck to the exhaust pipe: Replace the rear oxygen sensor with a new one.
TEST 4: Manually Inducing A Rich Air/Fuel Mixture

In this final performance test of the rear O2 sensor, you'll manually induce a rich air/fuel mixture. This test is a whole lot easier and simpler compared to the previous one.
What you'll do is spray a bit of starting fluid into the throttle body while the engine is running.
To accomplish this test, you'll first need to remove the air duct that connects to the throttle body. Then, you'll spray the starting fluid right into the throttle body (with the engine running).
If the rear O2 sensor is functioning correctly, its voltage output should spike to 0.8 to 0.9 Volts on your scan tool.
These are the steps:
- 1
Remove the air duct hose from the throttle body.
- 2
Start the engine.
NOTE: For the accuracy of the test, let the engine idle for about 15 minutes before inducing the rich air/fuel mixture (in step 7). - 3
Connect your scan tool to your vehicle's diagnostic port.
- 4
Enter the Live Data function.
- 5
Scroll down to the rear oxygen sensor voltage reading (generally labeled as O2S12).
The O2S12 reading will show you the voltage activity of the rear oxygen sensor. - 6
After 15 minutes of the engine running, the voltage reading should oscillate between 0.100 and 0.900 Volts every few seconds.
If the reading shows a fixed value (that neither rises nor falls), don't worry. Proceed to the next step. - 7
Spray a bit of starting fluid into the throttle body with the engine running while watching the O2S12 reading on your scan tool's screen.
If you spray too much starting fluid, the engine will shut off. If this happens, simply restart the engine and start from step 1 (spraying less starting fluid this time).
As you're spraying the starting fluid, the voltage reading of the rear O2 sensor should rise to 0.800 to 0.900 Volts. - 8
Stop spraying the starting fluid.
- 9
The voltage reading should start to oscillate between 0.100 Volts to 0.900 Volts within a couple of seconds.
Let's examine your test result:
CASE 1: The voltage spiked to 0.900 Volts when spraying starter fluid into the vacuum hose. This is the correct and expected result.
You can conclude that the catalytic converter is bad and is the cause of the P0420 code if you have:
- Confirmed a P0420 diagnostic trouble code is stored in the computer's memory.
- Confirmed that the rear oxygen sensor reacts to a manually induced lean air/fuel mixture (TEST 3).
- Confirmed that the rear oxygen sensor reacts to a manually induced rich air/fuel mixture (this test section).
CASE 2: The voltage did NOT spike to 0.900 Volts when spraying starter fluid into the vacuum hose. This result tells you that the rear oxygen sensor is faulty and you need to replace it.

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!

