TEST 1: Checking For A Broken Catalytic Converter

For our first test, let's see if we can find out if the catalytic converter's internal filter element has broken into fragments.
If this filter element is busted, you'll notice a rattling sound when you give the converter a few taps with a rubber mallet.
IMPORTANT: Make sure to do this test only when the engine and the converter are totally cooled down to prevent burns. Do not perform this test if either the engine or the converter is hot!
Let's get started:
- 1
Lift the vehicle and place it on jack stands. You'll only be able to access the catalytic converter from below the vehicle.
IMPORTANT: Use jack stands to keep your minivan elevated. Don't rely on the jack alone to keep it lifted!
IMPORTANT: The engine and the catalytic converter should be completely cold before performing this test. - 2
Tap the catalytic converter.
When I perform this test, I use the palm of my open hand or a large rubber mallet. - 3
Listen for rattling noises when you tap the catalytic converter.
If the filtering element inside the catalytic converter is broken into pieces, you'll hear a rattling noise when you tap it.
Let's analyze your test results:
CASE 1: The filtering element is broken into pieces. This confirms that the catalytic converter is bad and needs to be replaced.
CASE 2: The filtering element is NOT broken into pieces. This is the correct and expected test result.
The next step is to check the performance of the rear oxygen sensor. For this test, go to: TEST 2: Checking The Performance Of The Rear Oxygen Sensor.
TEST 2: Checking The Performance Of The Rear Oxygen Sensor
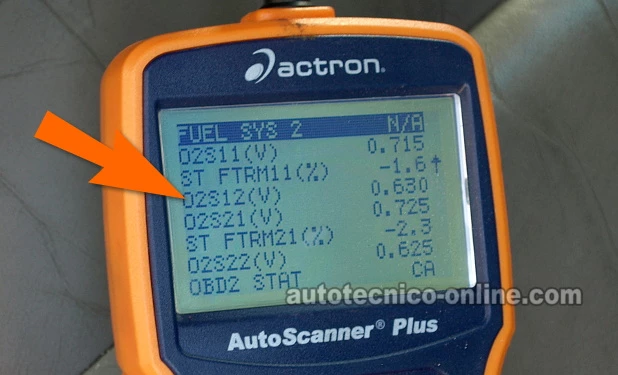
It's possible to evaluate how well the catalytic converter is working and we can do this by looking at the voltage output from the rear oxygen sensor.
The rear O2 (oxygen) sensor, also known as the downstream O2 sensor, is placed after the catalytic converter in the exhaust system. Its primary role is to monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter while the engine is running.
By analyzing the rear O2 sensor's output, we can figure out if the catalytic converter is still doing its job properly.
Specifically, if the rear O2 sensor outputs a constant voltage reading above 0.5 Volts (or 500 milliVolts), the converter isn't functioning as it should.
For this test, you'll need a scan tool that can show you 'Live Data' in real-time. Don't worry, you don't need to splurge on a high-end tool; a basic generic scan tool with 'Live Data' capabilities will get the job done.
Let's get started:
- 1
Connect the scan tool to your minivan's diagnostic port.
- 2
Start and run the engine.
NOTE: Let the engine idle for at least 15 minutes before moving on to the next step. This will allow the catalytic converter to activate. - 3
Once you're in the data stream function on your scan tool, look for the line identified as O2S12. This is where you can observe the 'live' output voltage reading of the rear oxygen sensor.
NOTE: It's the rear oxygen sensor that reports the activity of the catalytic converter. - 4
Take a look at the voltage reading of the rear oxygen sensor.
The voltage should fluctuate between 100 milliVolts to 500 milliVolts (0.1 to 0.5) while the engine is running.
NOTE: Unlike the front oxygen sensor, whose output signal constantly and rapidly varies between 100 milliVolts and 900 milliVolts (0.1 to 0.9), the reading from the rear oxygen sensor generally varies between 100 milliVolts and 500 milliVolts.
Let's take a look at what your test results mean:
CASE 1: Oxygen sensor voltage is consistently above 0.5 Volts. This generally confirms that the catalytic converter has failed. But I suggest one more test to be sure.
The next step is to check the rear oxygen sensor itself to make sure it's not faulty. For the next test, go to: TEST 3: Manually Inducing A Lean Air/Fuel Mixture.
CASE 2: Oxygen sensor voltage IS NOT consistently above 0.5 Volts. This is generally the correct and expected result and usually indicates that, for the time being, the catalytic converter is working correctly.
I suggest you check the performance of the rear oxygen sensor with the following test: TEST 3: Manually Inducing A Lean Air/Fuel Mixture.
