
In this tutorial, I'll explain the process for testing the radiator fan motor step-by-step. This test procedure also applies to the condenser fan motor.
With your test results, you'll quickly figure out if the radiator and/or condenser fan motor is working properly or needs to be replaced.
NOTE: The radiator cooling fan motor is located on the driver's side of the radiator. The condenser fan is located on the passenger side.
Contents of this tutorial:
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 2.2L Toyota Camry: 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001.
Radiator Fan Switch Test: The cooling fan motors get activated by the coolant temp switch (located on the bottom tank of the radiator). This switch can easily be tested and this tutorial will help you with the test step-by-step:
These other tutorials may come in handy:
- Common Causes Of Engine Overheating (1992-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry).
- How To Test The Thermostat (1992-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry).
- How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (1990-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry, Celica).
Wiring Diagrams: You can find the radiator fan motor wiring diagrams here:
- Cooling Fan Circuit Wiring Diagram (1992-1996 2.2L Toyota Camry).
- Cooling Fan Circuit Wiring Diagram (1997-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry).
Symptoms Of A Bad Radiator Or Condenser Fan Motor
In your 1992–2001 2.2L Toyota Camry, a radiator fan switch activates the radiator and condenser fans (at the same time) when the switch reaches a specific temperature to keep the engine from overheating.
Over time, the radiator (or condenser) fan motor bearings can wear out, causing more friction on the motor shaft as it spins.
This increased friction forces the fan motor to draw more current to operate, which can eventually lead to the fan motor fuse blowing or the fan relay burning out. When this happens, the radiator or condenser fan may stop working properly.
Here are the most common signs of a bad radiator fan motor:
- Engine overheating: The engine overheats, especially in stop-and-go traffic or while idling, due to one or both fans not cooling the engine.
- Repeatedly blown fuse: A bad fan motor often causes its fuse to blow because it's pulling too much current.
- Failed radiator fan relay: The radiator fan relay may burn out if the fan motor is struggling to work properly.
- Unusual noises: Grinding or squealing noises from the fan motor can indicate worn-out bearings.
- Fan doesn't engage: The radiator (or condenser) fan fails to turn on when the engine reaches high temperatures.
Where To Buy The Cooling Fan Motor
The cooling fan motors on the 1997-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry aren't expensive parts. The following links will help you comparison shop and save a few bucks:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
NOTE: Not sure if the fan motor assembly above fits your particular 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry? Don't worry. Once you get to the site they'll make sure it fits by asking you the specifics of your particular vehicle. If it doesn't fit, they'll find you the one that does.
TEST 1: Testing The Amperage Draw Of The Fan Motor
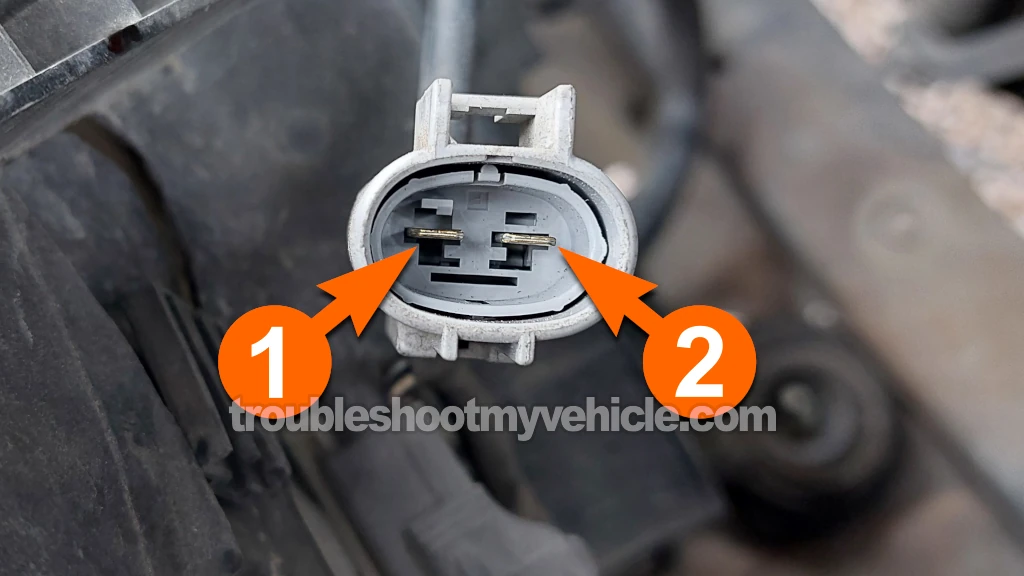

The first step in diagnosing the radiator (or condenser) fan motor is to check if it's drawing too much current —an obvious sign of a failing motor— by performing an amperage draw test.
Before starting, it's important to know the amperage rating of the fuses that protect the fan motors:
- Radiator Fan Motor Fuse (1992–2001): 30 Amp RDI Fuse (located in the under-hood fuse box on the left inner fender).
- Condenser Fan Motor Fuse (1992–2001): 30 Amp CDS Fuse (located in the under-hood fuse box on the left inner fender).
The thing to keep in mind here, is that the cooling system is designed so that when the fans run, they activate together and operate at either low speed or high speed.
- Low Speed: The fans run in series and draw current through a single fuse (the CDS 30A fuse).
- High Speed: The fans run independently, each drawing current through their respective fuses.
In practical terms, this means the combined amperage draw of both fan motors should never exceed 30 Amps. If it does, the CDS fuse will blow.
To test the fan motor's amperage draw, we'll:
- Use a multimeter set to Ohms mode to measure the motor's resistance.
- Apply Ohm's Law (Amps = Volts ÷ Ohms) to calculate the amperage draw.
IMPORTANT: Make sure the fan motor blades remain completely still while measuring resistance. Even slight movement can skew the reading and make the results inaccurate.
Let's dive in:
- 1
Disconnect the fan motor from its electrical connector.
- 2
Place your multimeter in Ohms mode.
- 3
Measure the resistance of the fan motor across pins 1 and 2 with your multimeter (see photo above).
NOTE: The test is done on the connector coming out of the fan motor. This connector has male spade terminals. - 4
Record the resistance value.
- 5
Repeat steps 1 thru 4 on the second fan motor.
- 6
Apply Ohms Law to calculate the amperage draw of each fan motor:
A.) Divide the resistance value of the first fan motor into 12.5.
B.) Divide the resistance value of the second fan motor into 12.5
To be a little more specific: If the resistance of a fan motor is 0.4 Ohms, the math would look like this: 12.5 ÷ 0.4 = 31.25. This means its amperage draw is 31.25 Amps. - 7
The calculated amperage draw of each fan motor must not exceed 15 Amps.
- 8
Add the amperage draw values of both fan motors.
- 9
The combined amperage draw of both fan motors should not exceed 30 Amps.
Let's interpret your test results:
CASE 1: The amperage draw of each motor is under 15 Amps and the combined amperage draw of both fan motor is under 30 Amps. This the correct and expected test result.
The next step is to manually apply battery power and Ground, from your Toyota Camry's battery, to the fan motor itself. For this test go to: TEST 2: Applying Power And Ground To The Fan Motor.
CASE 2: The amperage draw of one fan motor is over 15 Amps. This result tells you that your Toyota Camry's fan motor is defective and needs to be replaced —even if it runs.
Here's why: When the fan motor draws more than the specified current, it's a sign that its internal components, such as the bearings or windings, are worn out. This excess current can and will blow the fan motor fuse or burn out the relay.
So, even if the fan motor runs, its high amperage draw risks further damage to the cooling system and electrical components.
TEST 2: Applying Power And Ground To The Fan Motor
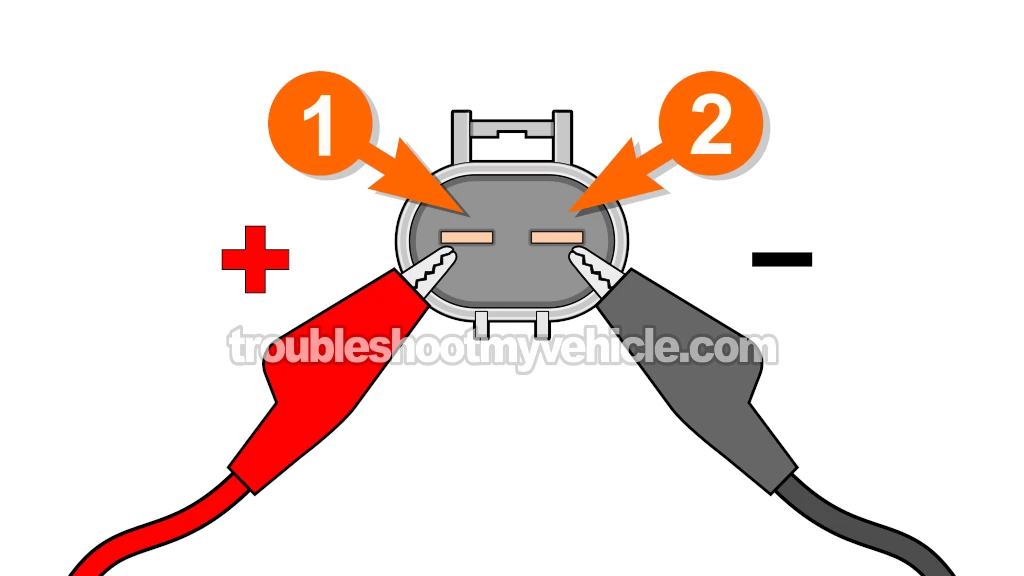
Now that you've verified the fan motor is drawing less than the specified amperage, it's time to proceed to the next test.
In this step, you'll use jumper wires to apply battery power and Ground directly to the radiator (or condenser) fan motor on your 2.2L Toyota Camry.
IMPORTANT: Perform this test only if the fan motor's amperage draw is less than 15 amps (as specified in TEST 1). If the amperage draw exceeds the fuse's rating, the fan motor is faulty —even if it runs when you apply battery power and Ground.
These are the test steps:
- 1
Disconnect the fan motor from its electrical connector.
The connector has 2 wires. The blue (BLU) wire supplies power and the black (BLK) wire supplies Ground. - 2
Apply battery power to the fan motor terminal identified with the number 1 in the illustration above.
You'll be applying power to the male spade terminal (of the radiator fan motor itself) that connects to the BLU wire of the electrical connector. - 3
Apply chassis Ground to the radiator fan motor terminal identified with the number 2 in the illustration above.
You'll be applying Ground to the male spade terminal (of the fan motor itself) that connects to the BLK wire of the electrical connector. - 4
The fan motor should run.
Let's take a look at your test results:
CASE 1: The fan motor ran. This is the correct test result.
You can conclude that your Toyota Camry's radiator (or condenser) fan motor is not defective if you have:
- Confirmed that the fan motor's amperage draw is not higher than the amperage rating of its fuse (TEST 1).
- Confirmed that the fan motor runs when applying 12 Volts and Ground to it (this test section).
The fan motor is activated by the coolant temp switch located on the bottom radiator tank. This tutorial will help you test it:
CASE 2: The fan motor DID NOT run. This test result tells you that the radiator (or condenser) fan motor is defective and needs to be replaced.
More 2.2L Toyota Camry Tutorials
You can find a complete list of 2.2L Toyota Camry tutorials and wiring diagrams in this index:
Here's a sample of the tutorials you'll find there:
- How To Test Engine Compression (1990-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry, Celica).
- How To Test The TPS With A Multimeter (1997-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry).
- How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (1990-2001 2.2L Toyota Camry, Celica).
- How To Test The Throttle Position Sensor (1992-1996 2.2L Toyota Camry).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!


