
One of the most common causes of an engine no-start problem is a bad ignition coil. The good news is that testing it is pretty easy.
I'm gonna break down my ignition coil test for you, step by step. With you test results, you'll know if the ignition coil as failed or if it's good.
NOTE: The ignition coil test I'm explaining in this tutorial is an on-car test of the coil. Some of the images I'm using show the distributor removed, but this is just so you can see the connections more clearly. Don't remove it to run these tests.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Ignition Coil Basics.
- What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition System?
- Where To Buy The Ignition Coil And Save.
- TEST 1: Checking The Spark Plug Wires For Spark.
- TEST 2: Checking The Ignition Coil For Spark.
- TEST 3: Checking The Distributor Cap For Spark.
- TEST 4: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Power.
- TEST 5: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Its Activation Signal.
- More 1.8L Toyota Corolla Tutorials.
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 1.8L (7A-FE) Toyota Corolla: 1995, 1996, 1997.
- 1.8L Geo Prizm: 1995, 1996, 1997.
Ignition System Wiring Diagrams:
- Ignition System Wiring Diagram (1995 1.8L Toyota Corolla).
- Ignition System Wiring Diagram (1996-1997 1.8L Toyota Corolla).
Ignition System Tests:
- How To Test The Igniter (1995-1997 1.8L Toyota Corolla).
- How To Test The Distributor Pickup Coil (1995-1997 1.8L Toyota Corolla).
- How To Test The CKP Sensor (1995-1997 1.8L Toyota Corolla).
Engine No-Start Basics:
Other Ignition Coil Test Tutorials:
Ignition Coil Basics
Your Corolla's ignition coil plays a major role in getting the engine started since its job is to take 12 Volts and ramp it up into the high voltage needed to create a spark across the spark plug electrodes. That spark then ignites the air/fuel mixture inside the cylinders.
Here's how it all goes down:
- Pickup coil and CKP sensor signals: When you turn the key to crank the engine:
- The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor starts generating its signal.
- The pickup coil inside the distributor generates a camshaft position (CMP) signal, known as the G signal in Toyota tech-speak.
- Igniter activation: Once it gets the signals, the computer knows you're cranking the engine and sends an activation signal to the igniter (also called the ignition control module).
- Ignition coil activation: The igniter switches the ignition coil on and off, allowing the coil to take the 12 Volts it's getting and ramp them up into a high-voltage charge.
- Distributor cap and rotor: That high voltage moves through the distributor cap and rotor, heading toward the spark plugs.
- Spark plug ignites the air/fuel mixture: The high voltage jumps the spark plug electrode gap, creating a spark that ignites the air/fuel mixture inside the cylinder.
- Engine starts: With all four cylinders getting spark and igniting their air/fuel mixtures, the engine comes alive.
The key thing to remember when troubleshooting the ignition coil is that it won't work without both battery power and an activation signal from the igniter. If either one's missing, no spark, no-start.
What Tools Do I Need To Test The Ignition System?
The three tools you'll need to test the ignition coil on your 1995-1997 1.8L Toyota Corolla are:
- Spark tester: This is a must-have tool to get an accurate spark test result. There are plenty to choose from, but I recommend the OTC HEI spark tester. You can check it out and buy it here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester (at: amazon.com).
- Multimeter: A multimeter is gonna help you confirm if the ignition coil's getting power (TEST 4). If you don't have one, here's the one I recommend: Tekpower TP8268 AC/DC Auto/Manual Range Digital (at: amazon.com).
- 12V automotive test light: This test light will help you check whether the ignition coil is getting its activation signal in TEST 5. If you need one, this is the one I use and recommend: Lisle 28400 Heavy Duty 12 Volt Test Light (at: amazon.com).
Where To Buy The Ignition Coil And Save
I'm recommending the Standard Motor Products UF204 Ignition Coil as the one you should purchase, since it's a well-known after-market brand. Once you get to amazon. Com thru the links below, you can also choose other brands too!
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
NOTE: Not sure if this ignition coil fits your Corolla? No worries! When you click the link and head to the site, they'll ask for your car's details to make sure it matches. If it doesn't, they'll help you find the right one.
TEST 1: Checking The Spark Plug Wires For Spark
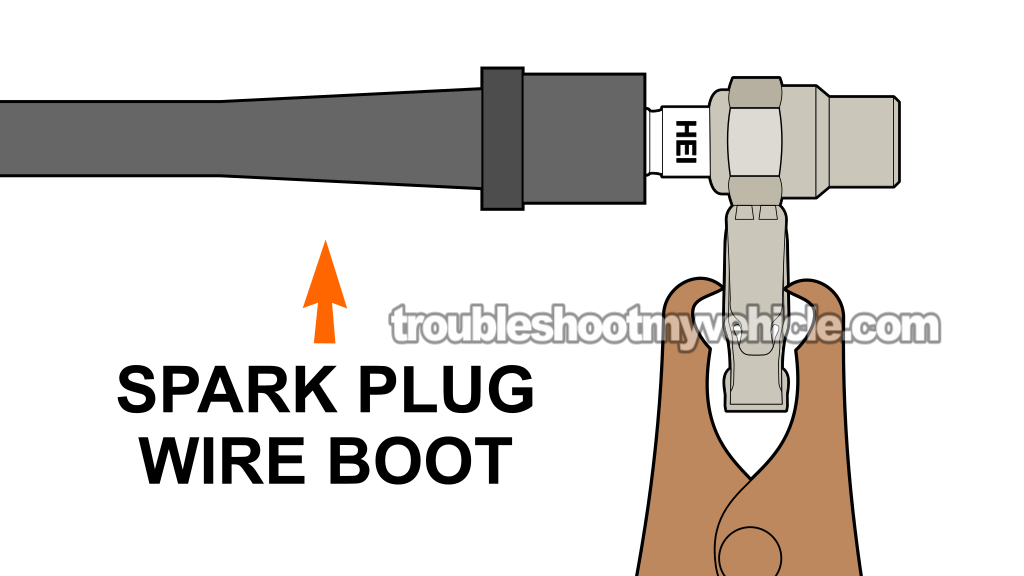
Alright, to kick things off, we're gonna start by testing for spark at each of the four spark plug wires.
This spark test will helps us confirm whether a lack of spark is really what's keeping your Corolla from starting.
For the most accurate results, you should use a dedicated spark tester. I personally recommend the OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester —it's the one I use, and the best part? No need to tweak any settings, it just works. You can check it out and buy it here: OTC 6589 Electronic Ignition Spark Tester (at: amazon.com).
Alright, let's begin:
- 1
Unplug the spark plug wire from the #1 cylinder's spark plug.
- 2
Connect the spark tester to the end of the spark plug wire.
- 3
Grab a battery jump-start cable and Ground the spark tester directly to the battery's negative (-) terminal.
- 4
Get someone to crank the engine while you keep your eyes on the spark tester.
- 5
You'll see one of two things: The spark tester spark or it doesn't spark.
- 6
Unplug the spark tester from the wire and plug the wire back onto the spark plug.
- 7
Repeat steps 1 through 6 for every spark plug wire.
Here's what your test results mean:
CASE 1: All four spark plug wires sparked. That's exactly what you wanna see! It confirms the ignition system isn't the reason your engine won't start.
You can also cross these parts off your suspect list:
- The igniter (ignition control module).
- The ignition coil.
- The pickup coil (inside the distributor).
- The CKP sensor.
- The distributor cap and rotor.
- The spark plug wires.
If the engine still refuses to start, the problem isn't with the ignition coil or anything in the ignition system.
CASE 2: Some spark plug wires sparked, but others didn't. That's usually a sign of bad spark plug wires or a worn-out distributor cap.
To dig a little deeper into this, go to: TEST 3: Checking The Distributor Cap For Spark.
CASE 3: None of the spark plug wires sparked. This test result confirms that the engine no-start is caused by a lack of spark.
Next step? We gotta check if the ignition coil itself is sparking. Head over to: TEST 2: Checking The Ignition Coil For Spark.
TEST 2: Checking The Ignition Coil For Spark

The ignition coil sits inside the distributor and fires the spark straight into the distributor cap.
The distributor cap then sends that spark to the rotor, which then transfers it to the metal terminals inside the cap.
From there, the spark travels through the distributor cap towers, down the spark plug wires, to its final destination: the spark plugs.
In this test section, we're gonna take off the distributor cap and check for spark right at the ignition coil with a spark tester.
- If the ignition coil sparks: The distributor cap or rotor is bad, blocking the spark and stopping the engine from starting.
- If there's no spark: We'll move on to TEST 4 to keep troubleshooting the ignition coil.
IMPORTANT: As you perform this test, make sure the distributor rotor spins when the engine cranks. If it doesn’t move, the timing belt's is broken —and that’s why the engine won’t start.
Alright, here's what you gotta do:
- 1
Remove the distributor cap from the distributor.
NOTE: Keep the distributor connected to its electrical connector while testing. - 2
Hook up the spark tester to the ignition coil's metal terminal.
NOTE: The spark tester might come loose while cranking the engine. To avoid that, wrap the tester and coil terminal together with black electrical tape to keep a firm metal-to-metal connection. - 3
Use a jump-start cable to Ground the spark tester straight to the battery's negative (-) terminal.
- 4
Have your helper crank the engine while you watch the spark tester.
- 5
You'll get one of two results:
1.) The spark tester sparks.
2.) The spark tester does not spark.
Here's what your test results mean:
CASE 1: The spark tester sparked. That's exactly what you wanna see.
If you've already confirmed:
- None of the four spark plugs sparked (from TEST 1).
- The ignition coil is producing spark (from this test).
Then the reason your spark plug wires aren't sparking is likely a bad distributor cap or rotor. Replacing them should fix the issue.
If the spark plug wires are just as old as the distributor cap and rotor, now's a good time to swap them out too.
CASE 2: The spark tester DID NOT spark. No spark usually means one of these problems:
- The ignition coil is faulty.
- The ignition coil isn't getting power.
- The ignition coil isn't receiving an activation signal from the igniter.
We now need to make sure the ignition coil is getting power. Go to: TEST 4: Making Sure The Ignition Coil Is Getting Power.


