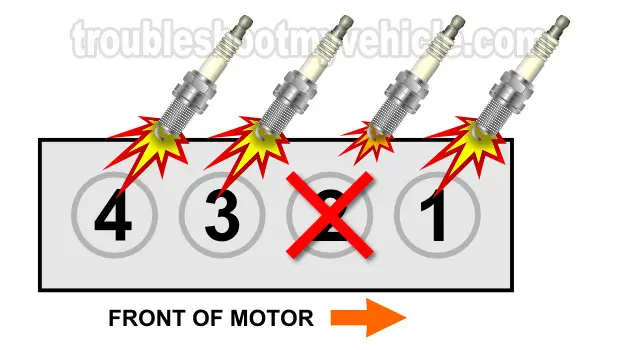
Finding the root cause of a cylinder misfire starts with identifying which one is the 'dead' cylinder. Once identified, you can find out what is missing (spark, or fuel, or compression) and causing the misfire.
For most cases, and if your 1.5L Honda Civic is OBD II equipped, you can check for misfire codes. For those times when checking for misfire codes is not an option or the vehicle doesn't have this capability, a manual cylinder balance test is the answer.
NOTE: This tutorial only covers 1.5L multi-port fuel-injected engines (in other words, the Honda engines with one fuel injector per cylinder).
Contents of this tutorial:
ES ![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Hacer la Prueba Balance de Cilindros (1.5L Honda Civic) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Hacer la Prueba Balance de Cilindros (1.5L Honda Civic) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 1.5L Honda Civic: 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995.
CYLINDER MISFIRE DIAGNOSTICS: If you're troubleshooting a rough idle or a cylinder misfire problem, the guide below is a must read:
Cylinder Balance Test
In a nutshell, a manual cylinder balance test involves 'killing' one cylinder at a time by disconnecting and reconnecting its fuel injector while the engine is running on your 1.5L Honda Civic.
Unplugging the fuel injector from its connector, while the engine is running, has one of two effects: either the engine's RPMs drop or they don't.
If the cylinder is 'dead' to begin with, unplugging the fuel injector will not cause any change whatsoever in the RPMs and you won't notice any change in the hum of the engine's idle.
Personally, to get a more accurate test result, I connect a vacuum gauge to a vacuum hose (on the engine) that has vacuum (when the engine is running) with a plastic T. As I disconnect and reconnect each fuel injector, I can see if the vacuum gauge's needle reacts or not. Now, this step is not necessary/critical, so if you don't have a vacuum gauge or can't get a hold of one, you don't need to worry about it.
OK, this is what you need to do:
- 1
Connect your vacuum gauge.
- You can use a plastic 'T' connector to connect your vacuum gauge to the fuel pressure regulator's vacuum supply hose.
- NOTE: Remember, using a vacuum gauge is not an absolute must.
- 2
Crank and start the engine..
- NOTE: Take all necessary safety precautions while working around a running engine.
- 3
Disconnect and reconnect one fuel injector at a time.
- When you disconnect the fuel injector, you should hear and feel a drop in the engine's idle (RPMs).
- If you also have a vacuum gauge connected, you'll see the gauge's needle drop.
- If the cylinder was 'dead' to begin with for any reason (not getting spark, low compression, etc.), you won't hear/feel a drop in the engine's idle (RPMs).
- 4
Repeat the test on the same cylinder.
- You can repeat this test as many times as you need to make sure of your test result.
- 5
Reconnect the fuel injector and test the next one.
- Perform the test on all of the 4 fuel injectors.
- 6
Interpret the results. After testing all cylinders, now you need to interpret the results.
CASE 1: Unplugging the fuel injector caused a drop in the RPMs. This tells you that the specific cylinder you tested is OK and not the cause of the misfire (miss or 'dead' condition).
More specifically, this test result lets you know that the fuel injector, spark plug, spark plug wire are OK for that specific cylinder.
CASE 2: Unplugging the fuel injector DID NOT cause a drop in the RPMs this tells you that the specific cylinder you tested is 'dead'.
The cylinder could be 'dead' for a number of reasons. For example:
- Bad spark plug (broken, severely worn out, carbon tracks, etc.)
- Bad spark plug wire.
- Bad distributor cap.
- Low engine compression.
- Bad fuel injector.
Don't let this big list of 'possibles' worry you, because one of the most important things you've accomplished with the cylinder balance test, is to find out which cylinder is the 'dead' one and this narrows down and focuses your troubleshooting efforts.
You'll find a list of articles that will further help you track down the problem that's causing that specific cylinder to Misfire here: Misfire Troubleshooting Guide.
NOTE: Every now and then, I've seen cases where the engine has a rough idle condition and I mean it's shaking all over the place... When I've done the cylinder balance test, unplugging each fuel injector did not cause any change/drop in the RPMs. Why? This is because whatever is causing the rough idle or miss is affecting all cylinders evenly.
Although it's beyond the scope of this article to test such a condition, I can tell you that the most likely culprit behind this type of problem is a leaking intake manifold causing the air/fuel mixture to lean out. Among other things:
- Fuel pressure regulator is leaking fuel into its vacuum hose/line.
- EGR valve stuck open (if the applicable).
- Fuel pump that's outputting insufficient fuel volume/pressure.
- Major vacuum leak.
- Low engine compression across all cylinders.
Misfire Troubleshooting Guide
Each cylinder needs air, fuel, and spark to produce power. So, when an engine cylinder is misfiring, it's missing one of these 3 key ingredients.
This also means that the 3 areas the misfire is most likely to occur are:
- Ignition system. Components that can cause a misfire are:
- Bad distributor cap.
- Bad spark plug.
- Bad spark plug wire.
- Engine oil leaking onto the spark plugs from the valve cover.
- Fuel system. Components that can cause a misfire are:
- Bad fuel injector.
- Fuel injector not getting activation pulses. Either because the PCM is bad or there's a short in the wiring between it and the PCM.
- Engine Mechanical. Problems that can cause a misfire:
- Low engine compression.
The above list may seem like troubleshooting a 'dead' (misfiring) cylinders is hard but with a good diagnostic strategy, you'll be able to find the root cause of the misfire.
Here are my suggestions (and the diagnostic strategy I use):
- Test the ignition system first.
- The ignition system is usually the culprit behind most of the misfire ('dead' cylinder) conditions.
- The following tutorial will help you test the ignition system on your 1.5L Honda Civic: How To Test The Igniter, Ignition Coil Accord, Civic, CRV, and Odyssey (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- Test the fuel injectors second.
- After eliminating the ignition system as the cause of the misfire, the next step is to make sure that the fuel injector is not fried internally.
- The following tutorial will help you do a fuel injector resistance test: How To Test The Fuel Injectors (1992-1995 1.5L Honda Civic).
- Test the engine compression third.
- After making sure that the ignition system is providing spark and the fuel injector is injecting fuel into the 'dead' cylinder, the next step would be to check that cylinder's compression.
- The following tutorial will help you do an engine compression on your 1.5L Honda Civic: How To Test Engine Compression (1992-1995 1.5L Honda Civic).
The above list of tests can be modified to suit your particular diagnostic, troubleshooting needs (since there really isn't a specific cookie cutter way of diagnosing a car).
More 1.5L Honda Civic Tutorials
I've written quite a few 1.5L Honda Civic diagnostic tutorials and you can find them all in this index:
Here's a sample of the tutorials you'll find in the index:
- How To Test The PGM-FI Main Relay (1992-1995 1.5L Honda Civic).
- How To Test The Fuel Injectors (1992-1995 1.5L Honda Civic).
- How To Test The Fuel Pump (1992-1995 1.5L Honda Civic).
- How To Test For A Broken Timing Belt (1992-1995 1.5L Honda Civic).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!


