TEST 2: Making Sure The CMP Sensor Is Getting 5 Volts
So far, your TEST 1 result confirms the CMP sensor isn't producing an ON/OFF signal.
In this test section, we'll verify that the camshaft position (CMP) sensor is getting its required 5 Volt power supply.
Without this voltage, the sensor can't generate a signal —and you'll likely see P0340 (or sometimes P0344 for an intermittent issue).
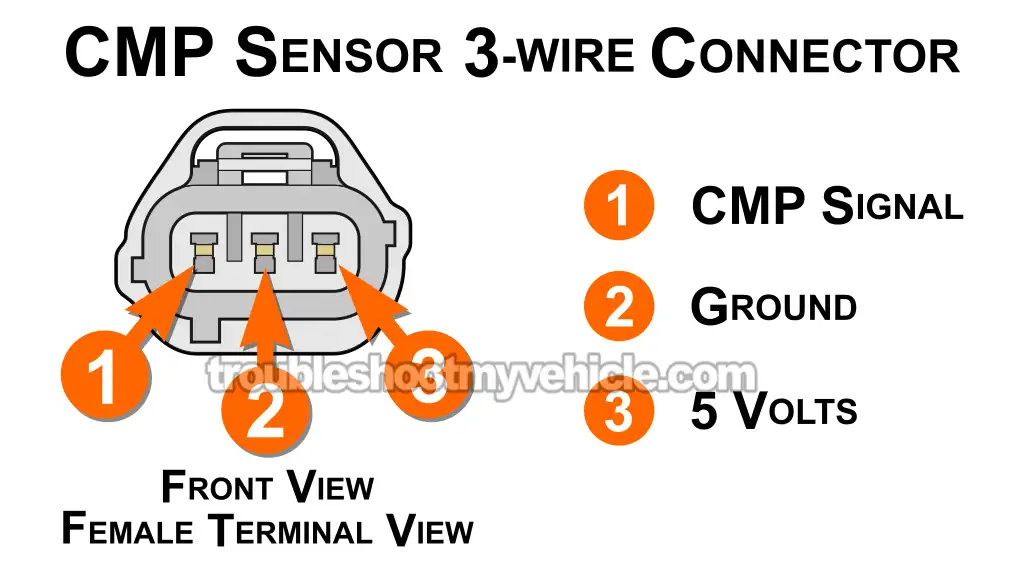
The 5V supply comes from the PCM and arrives at terminal 3 of the CMP sensor connector. This terminal connects to:
- 2002: orange (ORG) wire.
- 2003: violet with white stripe (VIO/WHT) wire.
- 2004-2007: yellow with pink stripe (YEL/PNK) wire.
Ready? Here's what to do:
- 1
Disconnect the CMP sensor connector.
- 2
Set your multimeter to DC Volts mode.
- 3
Connect the black multimeter lead to the battery negative (-) post.
- 4
Probe terminal 3 on the connector with your red multimeter lead.
NOTE: Double-check that terminal 3 actually connects to the YEL/PNK (VIO/WHT or ORG) wire. - 5
Turn the ignition key ON but don't crank the engine.
- 6
Your multimeter should show 4.5 to 5 Volts.
How to read your results:
CASE 1: 4.5 to 5 Volts present. This is the correct result and confirms the PCM is delivering the power to the CMP sensor.
Your next test is to confirm the CMP sensor has Ground. Move on to: TEST 3: Making Sure The CMP Sensor Is Getting Ground.
CASE 2: No voltage (0V). First double-check your test connections and repeat the test.
If the reading still shows 0V, the CMP sensor isn't getting the power it needs —and can't produce an ON/OFF signal, which will trigger P0340.
In most cases, this points to an open or broken section of the PNK/YEL wire between the PCM and sensor —not a faulty sensor. Repairing the wiring will restore the CMP signal and clear P0340.
TEST 3: Making Sure The CMP Sensor Is Getting Ground

Up to this point, your test results confirm two things:
- TEST 1: No ON/OFF voltage signal coming from the CMP sensor.
- TEST 2: The PCM is supplying proper 5 Volt power to the sensor.
Now it's time to check the Ground side of the CMP sensor circuits. The CMP gets Ground through terminal 2 of its connector. Specifically:
- 2002-2003: black with light blue stripe (BLK/LT BLU) wire.
- 2004-2007: dark blue with dark green stripe (DK BLU/DK GRN) wire.
Without this Ground, the sensor won't produce a signal —which can easily trigger P0340.
IMPORTANT: Never apply direct battery power to this wire —it will fry the PCM. The test I'm outlining below is a safe and effective way to confirm the presence of Ground.
How to test the CMP Ground path:
- 1
Disconnect the CMP sensor connector.
- 2
Set your multimeter to DC Volts mode.
- 3
Connect your red multimeter lead to battery positive (+) post.
- 4
Probe terminal 2 with the black multimeter lead.
NOTE: Double-check that terminal 2 connects to the DK BLU/DK GRN (or BLK/LT BLU) wire. - 5
Turn the key to ON (engine OFF).
- 6
You should see 10 to 12 Volts on the multimeter.
Here's what your test result means:
CASE 1: Multimeter registers 10 to 12 Volts. That's exactly what you want —the PCM is providing a good Ground.
If you've already verified 5V power and Ground (TEST 2 and this one), but still have no CMP signal (TEST 1), the sensor itself is faulty —and that's what's triggering P0340.
Below are two CMP sensors I personally recommend. They’re reliable, fit like the original, and come from brands I trust —so you don’t waste money on a knockoff that might fail early:
- Walker Products 235-1232 CMP Sensor (Amazon affiliate link).
- Standard Motor Products PC244 CMP Sensor (Amazon affiliate link).
Buying through these links helps support this site at no extra cost to you —thank you for helping keep these in-depth tutorials free.
CASE 2: 0 Volts / no reading. Double-check your test connections and repeat the test.
If the reading stays at zero, the Ground path is open —most likely a break in the DK BLU/DK GRN wire between the PCM and the sensor. This wiring issue must be fixed to restore sensor function and clear P0340.
More 4.7L V8 Dodge Ram Pickup Tutorials
You can find a complete list of 4.7L V8 Dodge Ramp pickup tutorials in this index:

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!

