The fuel pump in your 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram pickup is gonna fail sooner or later. When it does, you'll have either an engine no-start problem or engine performance issues.
Thankfully, checking the fuel pump's performance isn't difficult and in this tutorial, I'll show you how with a fuel pressure test gauge.
I'm also gonna cover how to use starting fluid to help you figure out if your engine's not starting due to a lack of fuel.
Contents of this tutorial:
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following Dodge Ram pickups:
- 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram 100 Pickup: 1992, 1993.
- 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram 150 Pickup: 1992, 1993.
- 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram 250 Pickup: 1992, 1993.
- 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram 1500 Pickup: 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001.
- 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram 2500 Pickup: 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001.
Fuel Pump Circuit Wiring Diagram:
- Fuel Pump Circuit Wiring Diagram (1992-1993 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram Pickup).
- Fuel Pump Circuit Wiring Diagram (1994-1995 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram Pickup).
- Fuel Pump Circuit Wiring Diagram (1996-1997 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram Pickup).
- Fuel Pump Circuit Wiring Diagram (1998-2001 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram Pickup).
Symptoms Of A Bad Fuel Pump
When the fuel pump fails, it'll usually do so in one of two ways:
- Complete failure: The pump gives out completely and fuel no longer reaches the fuel injectors. Your pickup's engine is gonna crank but not start.
- Degraded performance: The pump still works, but it only sends enough fuel to get the engine started. Once you stick the transmission in Drive, and step on the gas, the engine runs badly.
If the fuel pump isn't totally dead yet (where you're still able to start the engine), you'll notice one or more of the following symptoms:
- Rough idle: The engine will run rough or uneven at idle when it's not getting enough fuel.
- Hard starting: The engine only starts after cranking it for a while.
- No power: You'll feel a lack of power most when you're on the road and trying to speed up —your pickup just won't move like it should.
- Backfires: These are "popping" sounds heard through the intake manifold when you hit the gas but the engine isn't getting enough fuel.
- Running lean: A lean air/fuel mixture will result from a fuel pump that isn't sending enough fuel to the engine. This can trigger oxygen sensor or lean air/fuel mixture diagnostic trouble codes.
Doesn't matter if your Ram won't start at all or just runs like crap —a quick fuel pressure test can tell you if the pump's the problem.
What does "lean" mean? For the engine to run smoothly, it needs the right balance of air and fuel —this is known as the air/fuel mixture. The fuel injection system is responsible for adding the correct amount of fuel depending on how much air is entering the engine at any given moment. If it's unable to add enough fuel (like when the fuel pump is failing) for the amount of air, the air/fuel mixture is called "lean".
If the opposite happens, and the system adds too much fuel for the amount of air coming in, the mixture is called "rich".
Fuel Pressure Specifications
| 1992 |
|---|
| 39 PSI (Key On Engine Off -KOEO) |
| 1993 |
|---|
| 31 PSI (Key On Engine Off or Key On Engine Running with vacuum hose connected to fuel pressure regulator) |
| 8-10 PSI higher with Engine Running and vacuum hose disconnected to fuel pressure regulator) |
| 1994-1995 |
|---|
| 35-45 PSI (Key On Engine Running At Idle -No Load) |
| 1996-2001 |
|---|
| 44-54 PSI (Key On Engine Off -with scan tool activating the fuel pump) |
NOTE: If your Dodge Ram pickup does not start and there's only a Key On Engine Running (KOER) fuel pressure specification, then that KOER specification will apply to your Key On Engine Off (KOEO) fuel pressure test.
Where To Buy A Fuel Pressure Test Gauge
You can buy a fuel pressure test gauge just about anywhere and is one of the most important tools any serious DIY'er should have in his/her tool box.
The following fuel pressure test gauge kits are pretty good deals and will work with your Dodge Ram Pickup:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
TEST 1: Checking Fuel Pressure With A Fuel Pressure Gauge
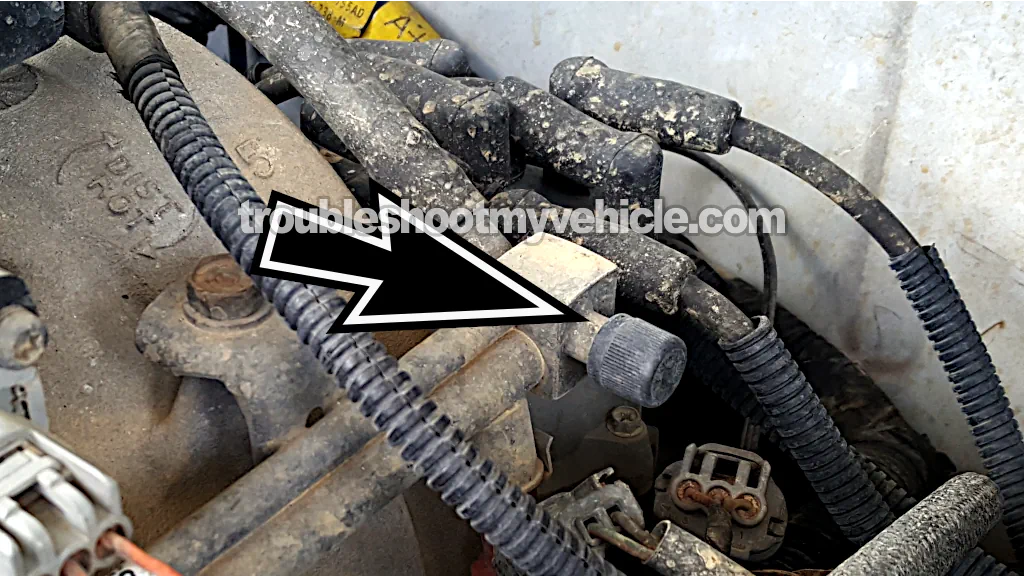
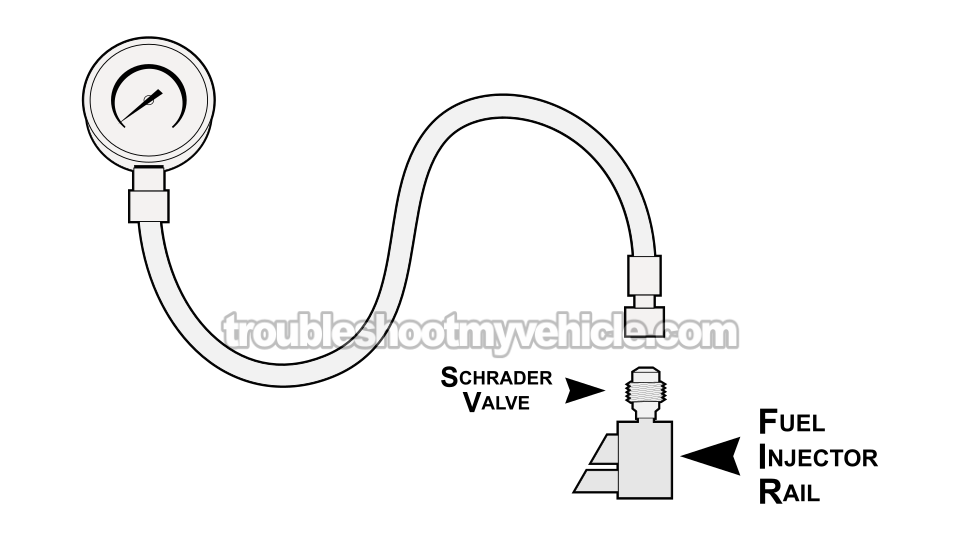
To check your fuel pump's pressure, you'll need to connect a fuel pressure test gauge to the Schrader valve.
The Schrader valve is located on the fuel injector rail, toward the back of the engine on the driver's side, close to the distributor and right next to the fuel injector for cylinder #5 (see image 2 of 2 above).
It looks like a bigger version of the air valve stem you use to air up a bicycle tire —yup, it's the same type of valve.
It also works the same way (as the one on a bike tire), but it's made specifically to test your Dodge Ram pickup's fuel pump pressure.
NOTE: This tutorial covers 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram pickups made over nine years, so don't worry if your Schrader valve doesn't look just like the one in image 2 of 2 (in the image viewer), it'll be in the same corner of the engine and look similar.
IMPORTANT: The 1996-2001 models require that you use a scan tool to activate the fuel pump to check the fuel pressure with the Key On Engine Off (KOEO). If you have such a scan tool -awesome. If you don't, don't worry. The test steps below, in the part "KOEO only", workaround this requirement by disconnecting the ignition coil from its connector and cranking the engine.
Okay, here's what we're gonna do:
- 1
Wrap a shop towel around the Schrader valve.
The shop towel will catch any fuel that might/will leak in the next step. - 2
Connect your fuel pressure gauge to the Schrader valve (see image 1 of 2 and image 2 of 2).
- 3
Have your helper switch the key on and off rapidly several times (but don't crank the engine) while you keep an eye on the gauge.
If you see any fuel leaking where you connected the gauge, tighten the connection a little more by hand to stop it.
Key On Engine Running (KOER) Only:
- 4
Start the engine and take a look at the pressure gauge.
- 5
Your gauge should hit the right pressure for your model.
Click here: Fuel Pressure Specifications.
Key On Engine Off (KOEO) No Scan Tool Only:
- 4
Disconnect the ignition coil from its 2-wire electrical connector.
NOTE: This test applies to the models that only have a KOEO fuel pressure specification. - 5
Crank the engine and then let go of the key.
- 6
Your gauge should hit the right pressure for your model.
Click here: Fuel Pressure Specifications.
Key On Engine Off (KOEO) With Scan Tool Only:
- 4
Connect your scan tool to the diagnostic link connector (DLC).
- 5
Activate the fuel pump.
- 6
Your gauge should hit the right pressure for your model.
Click here: Fuel Pressure Specifications.
Let's break down what your pressure test result's telling you:
CASE 1: Gauge reads 0 PSI. This confirms that no fuel is reaching the engine.
In almost every case, the fuel pump's bad and needs to be replaced. But in rare cases, it's just not getting power.
I recommend that you also check that the pump's getting between 10–12 Volts DC while you're cranking to be absolutely sure.
CASE 2: Pressure's there, but it's lower than it should be. That means the pump's weak —it's struggling and gonna fail soon. Replace the fuel pump.
CASE 3: Pressure looks good. This tells you the pump's doing fine.
If the pressure's spot on but the engine still won't start, the fuel pump isn't behind the problem. You'll need to continue troubleshooting the engine performance or no-start issue elsewhere.
TEST 2: Using Starting Fluid To Confirm Lack Of Fuel

The fastest way to find out if your truck's not starting because it's not getting fuel (like from a bad fuel pump) is the starting fluid test.
This test involves spraying starting fluid straight into the throttle body, then cranking the engine and watching what happens.
If there's no fuel reaching the engine, it'll run for a few seconds off the starting fluid alone —then cut off once it consumes the starting fluid.
This method of checking for a bad fuel pump isn't super precise/accurate, but it can point your engine no-start diagnosis in the right direction.
NOTE: You'll only get an accurate test result if all six spark plug wires are firing spark. So if you haven't done it yet, make sure to check for spark before doing the starting fluid test.
IMPORTANT: After spraying starting fluid into the throttle body, set the air cleaner assembly back onto it before cranking the engine. You don't have to tighten the clamp. This safety precaution will keep any backfire from spouting flames out of the throttle body.
Here's how we're gonna do it:
- 1
Pull off the air cleaner assembly from the throttle body. No need to yank it all the way off —you'll put it back on in a second.
- 2
Open the throttle plate and spray some starting fluid into the bore.
- 3
Place the air cleaner assembly back over the throttle body. You don't have to tightening it's clamp.
- 4
Crank the engine once the air cleaner assembly is back on and you're standing clear.
- 5
You'll see one of two things:
1.) The engine starts up for a moment, then shuts off.
2.) It just cranks and never starts.
Here's what those results mean:
CASE 1: Engine started and ran for a few seconds. That points to a fuel problem —the fuel pump's probably not doing its job.
Your next step? Hook up a fuel pressure gauge and do a proper test. Go here: TEST 2: Checking Fuel Pressure With A Fuel Pressure Gauge.
CASE 2: Engine didn't start at all. That usually means a lack of fuel's not the issue.
But since this test isn't super exact, it's still smart to run a pressure check with a gauge to confirm. Head here: TEST 2: Checking Fuel Pressure With A Fuel Pressure Gauge.
More 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram Pickup Tutorials
I've written quite a few 3.9L V6 Dodge Ram pickup 'how to test' tutorials. You can find them in this index:

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!