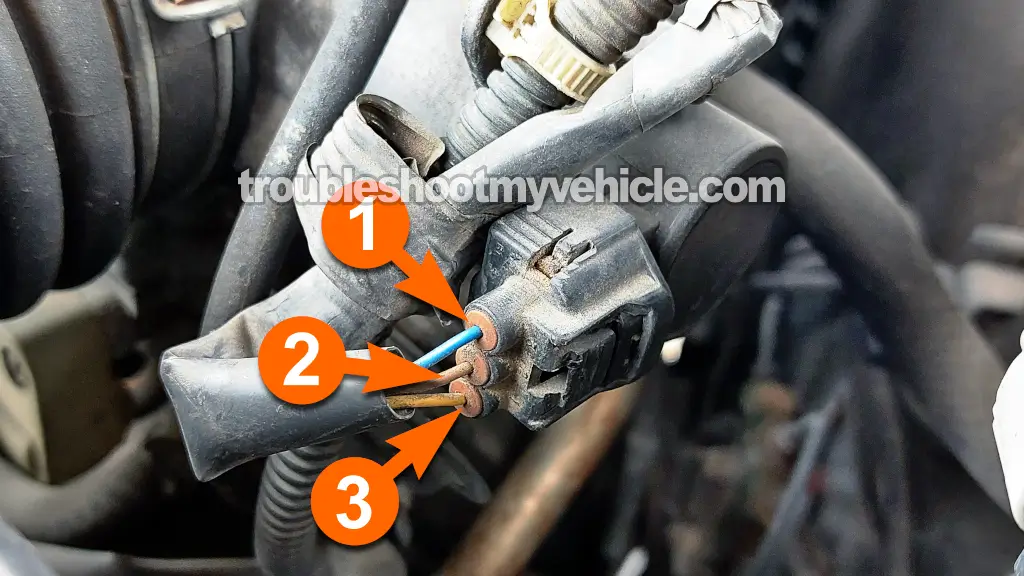
The throttle position sensor (TPS) on the 1997 through 2006 3.0L V6 Toyota Camry is a three wire sensor that can easily be tested with a multimeter.
That's right, you don't need a scan tool to be able to diagnose it as good or bad.
In this tutorial, I'll explain the three tests you can perform to find out if it's good or bad.
Contents of this tutorial:
NOTE: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 3.0L Toyota Camry: 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001.
- 3.0L Toyota Avalon: 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004.
- 3.0L Toyota Sienna: 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003.
- 3.0L Toyota Solara: 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002.
Symptoms Of A Bad Throttle Position Sensor
The throttle position sensor (TPS) is tasked with measuring the angle of the throttle plate inside the throttle body.
As you probably know, the throttle plate is linked to the accelerator pedal through an accelerator cable.
When you press the pedal, the throttle plate opens wider, allowing more air to enter the engine. Releasing the pedal causes the throttle plate to close, reducing the amount of air flowing in.
The fuel injection computer uses input from the TPS to track the throttle plate's position, making it an essential component of the fuel injection system.
If the TPS fails, it can lead to noticeable engine performance problems with your 3.0L Toyota Camry. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- The check engine light (CEL) is illuminated on the instrument panel.
- A TPS diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is stored in the PCM's memory:
- P0120: Throttle Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- P0121: Throttle Position Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem.
- Poor gas mileage.
- Hard starts or extended cranking time after shutting the engine off.
- Black smoke coming from the tailpipe.
- Hesitation when accelerating.
Circuit Descriptions Of The TPS

| Camry TPS Pinout | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
| 1 | Blue (BLU) | TPS Signal |
| 2 | Brown (BRN) | Sensor Ground |
| 3 | Yellow (YEL) | 5 Volts |
To properly diagnose the throttle position sensor (TPS), it's important to understand how it functions. The TPS produces a voltage signal that changes in response to the movement of the throttle plate. This signal helps the fuel injection computer keep track of the throttle plate's position.
- When the throttle plate is fully closed, the TPS usually sends a voltage signal ranging between 0.5 and 0.9 volts DC.
- As the throttle plate opens (for example, when you press the accelerator pedal), the voltage steadily increases. At full throttle, the signal typically reaches 4.5 to 5 volts DC, depending on the specific vehicle.
When the TPS fails, a common issue is that the voltage signal gets "stuck" at one value, regardless of the throttle plate's movement.
This causes the TPS to send incorrect information to the fuel injection computer, leading to performance problems since the computer can no longer accurately monitor the throttle plate's position.
Where To Buy Your TP Sensor And Save
Where can you buy the TP sensor for your 3.0L Toyota Camry? You can buy it at your local auto parts store but it's gonna' cost a whole lot more. I suggest taking a look at the price of the TP sensor in the following links and compare:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
Not sure if the above TP sensor fits your particular 3.0L Toyota Camry? Don't worry, once you get to the site, they'll make sure it fits by asking you the particulars of your vehicle. If it doesn't fit, they'll find you the right one.
TEST 1: Testing The Throttle Position Sensor Voltage Signal

The first thing we're going to do is check if the TPS is creating a variable voltage signal.
Specifically, we need to verify that the TPS voltage signal increases as we open the throttle plate and decreases as we close it.
In most cases, a faulty throttle position sensor will produce a voltage signal that stays stuck at one value, regardless of whether the throttle plate is opening or closing.
To test this, we'll connect our multimeter to the blue (BLU) wire in the TPS's three-wire connector. In the image above, this wire is labeled with the number 1.
IMPORTANT: For this test to work, the throttle position sensor must stay connected to its 3-wire connector. You'll need to use a back probe or a wire-piercing probe to access the TPS signal. You can see an example of this tool here (and where to buy it): Wire Piercing Probe.
Let's get started:
- 1
Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode.
- 2
Connect the red test lead to the BLU wire of the TP sensor's connector.
- 3
Ground the black multimeter lead directly on the battery negative (-) post.
- 4
Manually open the throttle plate.
You'll get the best results by opening and closing the throttle plate directly on the throttle body instead of stepping on the accelerator pedal. - 5
The multimeter should show an increasing voltage as you (or your helper) open up the throttle.
You'll get the best results by opening and closing the throttle plate directly on the throttle body instead of stepping on the accelerator pedal. - 6
The multimeter should show a decreasing voltage as you begin to close the throttle plate.
- 7
Using a screwdriver's handle, gently tap the TP sensor as you open and close the throttle plate and observe the multimeter.
The purpose (of tapping the TP sensor with the screwdriver's handle) is to see if the TP sensor shows gaps in the voltage signal. Why? Because a good TP sensor will show a continuous increasing or decreasing voltage signal even while getting tapped by the screw-driver's handle.
Let's examine your test results:
CASE 1: The voltage increased/decreased as you manually opened/closed the throttle plate. This test result confirms that the TP sensor is OK and not defective.
CASE 2: The voltage DID NOT increase/decrease as you manually opened/closed the throttle plate. This tells you that the throttle position sensor (TPS), on your Camry, has a problem.
Before condemning the TPS as bad, you need to make sure that it's getting both 5 Volts and Ground. For the next test, go to: TEST 2: Making Sure The TPS Has 5 Volts.
CASE 3: The multimeter DID NOT register any voltage. This test result doesn't condemn the TP sensor as bad just yet.
Why? Because the TP sensor may be missing either 5 Volts or Ground. So the next step is to check that the TP sensor is getting 5 Volts, go to: TEST 2: Making Sure The TPS Has 5 Volts.


