In this tutorial, I'll explain how to test the igniter (ignition control module) on the 1997–1998 1.5L Toyota Tercel.
This is an on-car test of the igniter -no need to remove it to test it. All of the test steps are explained in a step-by-step manner so that you can easily and quickly diagnose the igniter as good or bad.
Contents of this tutorial:
- Test The Ignition Coils For Spark First.
- Symptoms of Bad Igniter.
- Igniter Circuit Descriptions.
- Basic Operation Theory Of The Igniter.
- TEST 1: Making Sure The Igniter Is Getting Power.
- TEST 2: Making Sure The Igniter Is Getting Ground.
- TEST 3: Testing The Igniter Control Signals.
- TEST 4: Testing The Ignition Coil Control Signals.
- More 1.5L Toyota Tercel Tutorials.
WIRING DIAGRAM: You can find the ignition system wiring diagram here:
You can find the 1995-1996 1.5L Toyota Tercel igniter tests here:
Test The Ignition Coils For Spark First
Before testing the igniter, you'll need to first test the ignition coils for spark.
If both ignition coils are creating and delivering spark to the four engine cylinders, you can conclude that the igniter is functioning correctly (and you don't need to test it).
If you haven't already tested the ignition coils, please do so first. The following tutorial will help you determine if you need to come back here to test the igniter:
Symptoms Of A Bad Igniter
The ignition control module (igniter) is the component responsible for activating the ignition coils on your 1.5L Toyota Tercel.
When the igniter fails, it will stop activating one or both ignition coils. The end result is an engine no-start problem due to a lack of spark.
Igniter Circuit Descriptions
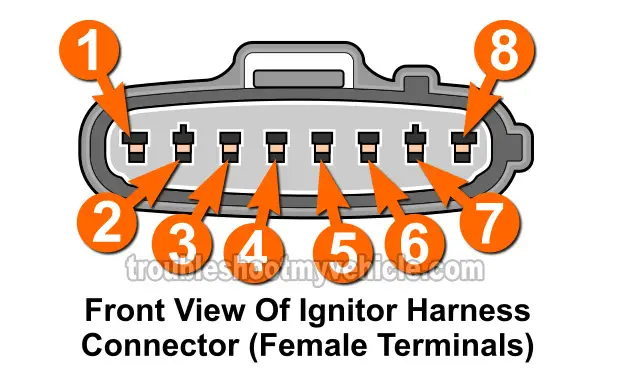
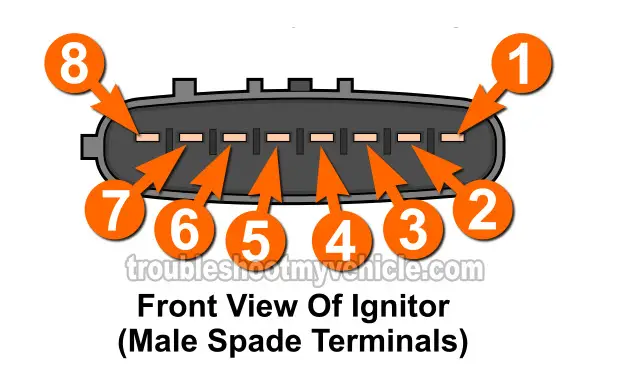
The igniter (ignition control module) has 8 wires coming out of its connector. Each one has a specific job to do and here's a brief description of each:
| 1995-1996 1.5L Tercel Igniter Connector | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
| 1 | Red with white stripe (RED/WHT) | IGC2 -2/3 Ignition coil control signal |
| 2 | Red with blue stripe (RED/BLU) | IGF -Ignition coil firing feedback |
| 3 | White with black stripe (WHT/BLK) | GND -Chassis Ground |
| 4 | Blue with yellow stripe (BLU/YEL) | IGT2 -Igniter control signal cylinders 2/3 |
| 5 | Gray (GRY) | IGT1 -Igniter control signal cylinders 1/4 |
| 6 | Black with blue stripe (BLK/BLU) | TACH -Tachometer signal |
| 7 | Black with white stripe (BLK/WHT) | +B -Battery power |
| 8 | Red (RED) | IGC1 -1/4 Ignition coil control signal |
NOTE: The igniter harness connector has female metal terminals. You'll need to use a back probe or a wiring piercing probe to test the signals in the wires.
Basic Operation Theory Of The Igniter
In a nutshell, when you turn the key and crank the engine:
- The igniter gets battery power (10 to 12 Volts DC) from female terminal #7 of its engine wiring harness connector (see illustration 2 of 2 above).
- The wire that feeds battery power to the igniter is the black with white stripe (BLK/WHT) wire.
- This same circuit also feeds battery power to the ignition coils.
- The crankshaft (CKP) and camshaft (CMP) position sensors start to generate their signals. These signals are transmitted directly to the fuel injection computer.
- Once the fuel injection computer gets the CKP and CMP position signals, it sends two igniter control signals to the igniter:
- IGT1 signal:
- The IGT1 signal relays the command to the igniter to activate the 1/4 ignition coil.
- It's received on terminal #5.
- The color of the wire is gray (GRY).
- IGT2 signal:
- The IGT2 signal relays the command to the igniter to activate the 2/3 ignition coil.
- It's received on terminal #4.
- The color of the wire is blue with yellow stripe (BLU/YEL).
- IGT1 signal:
- When the igniter receives the igniter control signals, it sends the ignition coils activation signals:
- IGC1 signal:
- The IGC1 signal is the activation signal for the 1/4 ignition coil.
- It's sent on terminal #8.
- The color of the wire is red (RED).
- IGC2 signal:
- The IGC2 signal is the activation signal for the 2/3 ignition coil.
- It's sent on terminal #1.
- The color of the wire is red with white stripe (RED/WHT).
- IGC1 signal:
- Once the ignition coils get their IGC1 and IGC2 signals, they start to spark away.