TEST 8: Testing The Power Transistor's Activation Signal
If you've reached this point you have confirmed that:
- None of the spark plug wires are delivering spark to the engine (TEST 1)
- The ignition coil is not sparking (TEST 4)
- The ignition coil is getting power (TEST 5)
- The ignition coil is not getting an activation signal (TEST 6)
- The power transistor is getting Ground (TEST 7)
For our last test we're going to make sure that the fuel injection computer is activating the power transistor.
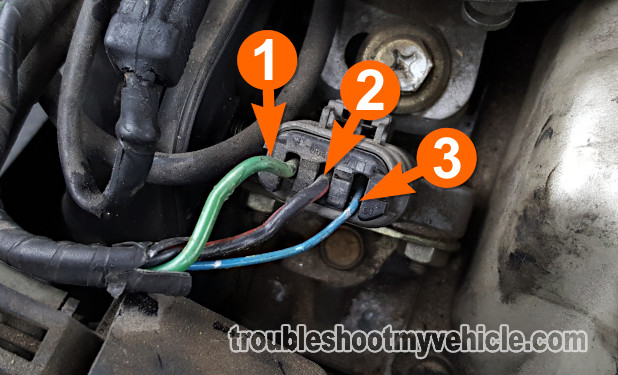
The power transistor receives an activation signal on the wire labeled with the number 3.
This wire is the blue wire of the power transistors 3-wire connector.
NOTE: The power transistor must be connected to its 3-wire connector for this test to work. To access the signal inside the wire you'll need to use a back probe or a wire piercing probe. You can see an example of this tool here: Wire Piercing Probe Review (Power Probe PWPPPPP01).
OK, let's get started:
- 1
Connect the red lead of the LED light to the BLU wire labeled with the number 1 in the photo above.
The power transistor must remain connected to its 3-wire connector. So you'll need to first connect a back probe or a wire piercing probe to the wire and then connect the red lead of LED light to this tool. - 2
Connect the black lead of the LED light to the battery negative (-) terminal.
- 3
Have an assistant crank the engine.
- 4
The LED light should blink ON and OFF as the engine cranks.
NOTE: Don't worry about what the LED light does before or after your helper starts cranking the engine. The only results you're interested in interpreting are the results obtained with the engine cranking.
Let's interpret your test result:
CASE 1: The LED light flashed ON and OFF. This is the correct test result and it lets you know that the fuel injection computer is supplying the power transistor with an activation signal.
You can conclude that the power transistor is fried and needs to be replaced only if you have:
- Confirmed that the ignition coil does not spark (TEST 4).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil is getting 10 to 12 Volts (TEST 5).
- Confirmed that the ignition coil activation signal is not present (TEST 6).
- Confirmed that the power transistor is getting Ground (TEST 7).
- Confirmed that the power transistor is getting its activation signal (TEST 8).
CASE 2: The LED light DID NOT flash ON and OFF. Without this activation signal the power transistor will not activate the ignition coil.
Recheck all of your connections. If the LED light does not flash ON and OFF, then this indicates that the camshaft position sensor (located inside your Nissan Quest's distributor) is defective.
The camshaft position sensor can be easily tested and you can find the tests explained here: How To Test The Camshaft Position Sensor (1993-1998 3.0L Nissan Quest).
Other Causes Of A Misfire

Quite a few things can cause the engine, in your 3.0L Nissan Quest (Mercury Villager) to misfire or idle rough.
If the ignition system components are not behind the misfire then I recommend the following tests:
- Check that the spark plugs are not covered or swimming in engine oil.
- Over time, this oil will cause carbon tracks to form on the spark plug's ceramic insulator and on the inside of the spark plug boot. The end result of this will be a misfire.
- The photo above shows what a carbon track looks like on the inside of the spark plug wire boot and on the ceramic insulator of the spark plug.
- The following is a real life case study of how carbon tracks can cause a misfire problem: Carbon Tracks Are A Common Cause Of Ignition Misfires (at: easyautodiagnostics.).
- Engine compression test.
- One of the most overlooked diagnostic tests to find the root cause of misfire is the compression test.
- You can find the engine compression test explained here: How To Test Engine Compression (3.0L Nissan) (at: easyautodiagnostics.).
- Broken spark plugs.
- This usually happens at tune-up time (if you have dropped one on the floor).
- You power washed the engine (this is something that should never be done on any Nissan vehicle).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!


