
Troubleshooting a misfire condition on your 3.0L V6 equipped Honda Accord (Acura CL) can seem quite intimidating and/or near impossible. Especially since quite a few things can cause one or more cylinders to go 'dead' such as:
- Failed ignition system component.
- One or more engine cylinders having very low compression.
- Bad fuel injector.
I could go on about more 'possible' bad components but you get the general idea. The good news is that testing a misfire code, or misfire codes, or a rough idle condition is not that hard and it's something you can do or learn enough to make an informed decision at your auto repair shop.
In this tutorial, I'm going to explain in some detail the most common causes of misfires and misfire codes (P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305, P0306 -OBD II equipped) and more importantly, I'm also gonna' offer you a simple diagnostic strategy that I'm certain will help you 'nail down' the cause of the misfire condition, misfire code, or rough idle condition your Honda is experiencing.
Contents of this tutorial:
ES ![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Una Falla En Cilindro (1995-2003 3.0L Honda Accord y Odyssey) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Una Falla En Cilindro (1995-2003 3.0L Honda Accord y Odyssey) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
APPLIES TO: This tutorial applies to the following vehicles:
- 3.0L V6 Honda Accord: 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007.
- 3.0L V6 Acura CL: 1997, 1998, 1999.
What Is A Misfire Condition?
In a nutshell, a misfire condition describes a situation in which one or more cylinders of your Honda's 3.0L V6 are not functioning. It can be said that this cylinder or cylinders are 'dead' either because the cylinder or cylinders are missing fuel, or spark, or air.
Here are a few other symptoms you'll see with a misfire:
- The check engine light will be on.
- One or more misfire codes (P0300-P0306) will be stored in your Honda's PCM memory (if OBD II equipped).
- P0300 Random Cylinder Misfire.
- P0301 Cylinder #1 Misfire.
- P0302 Cylinder #2 Misfire.
- P0303 Cylinder #3 Misfire.
- P0304 Cylinder #4 Misfire.
- P0305 Cylinder #5 Misfire.
- P0306 Cylinder #6 Misfire.
- Sometimes, even tho' your OBD II equipped Accord is suffering a bonafide misfire, no misfire codes are registered and no check engine light (CEL) comes on.
- Lack of power upon acceleration.
- Smell of unburned gas exiting the tail pipe.
- Rough idle and may stall.
- Cranks but does not start.
- Will not pass the emissions tests.
- Bad gas mileage.
Although the misfire codes don't tell you what exactly is the cause of the misfire or rough idle condition, there is a way to find out exactly what is causing it.
One of the most important things you need to know, to successfully diagnose a misfire or rough idle condition, is what causes a misfire. Let's go to the next subheading and find out.
What Tests Can I Perform To Find The Cause Of The Misfire Condition?
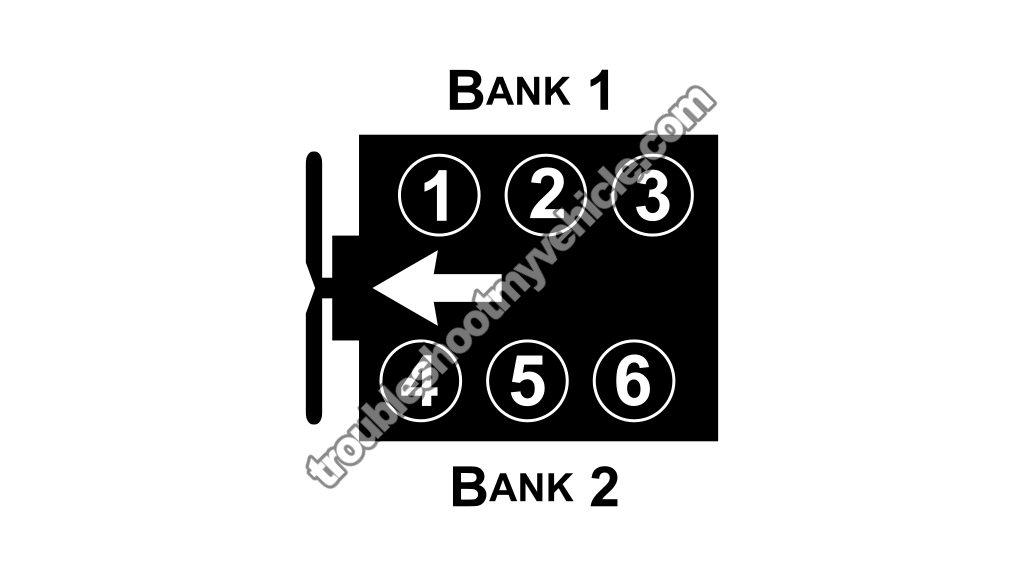
In the previous section we discussed that the misfiring cylinder will misfire (or go 'dead') due to a lack of fuel, or spark or air (compression), so you might be asking yourself, 'what do I start testing first?'.
Well, if I where in your shoes and I was the one troubleshooting the misfire, I'd start by first finding the 'dead' cylinder and then making sure that it was getting spark.
The following diagnostic strategy should help you find and resolve the root cause of the misfire or 'dead' cylinder on your 3.0L V6 Honda Accord:
STEP 1: Identify the dead cylinder.
- This can easily be done by reading the misfire diagnostic trouble codes stored in the PCM's memory with a code reader or a scan tool. Then by matching the misfire code to its engine cylinder using an illustration of the engine cylinders.
- If no misfire codes, even though the engine is suffering a bonafide misfire, you'll need to do a manual cylinder balance test by unplugging one fuel injector or one COP ignition coil at a time.
- The fuel injector or COP ignition coil that does not worsen the engine's idle when unplugged tells you that that specific cylinder is 'dead'.
STEP 2: Check that the 'dead' cylinder is getting spark. It's important to make sure that the misfiring cylinder is getting spark.
- This simply involves checking the spark plug wire (1998-1999) or the COP ignition coil (2000-2010) for spark with a spark tester.
- If the spark tester sparks, the cylinder misfire is not due to an ignition system issue.
- If the spark tester DOESN'T spark, you now know the ignition system is causing the issue.
- Distributor Ignition System: This tutorial is a good resource:
- COP Coil Ignition System: The following tutorials will help you:
STEP 3: Check the 'dead' cylinder's spark plug and spark plug boot. It's important to remove the spark plug and visually inspect for any problems or damage.
- Once the spark plug is removed, check it's electrodes for severe wear or any other obvious damage that'll keep it from sparking like cracks or carbon tracks on its ceramic insulator.
- You'll also need to see if the spark plug boot is swimming in oil or has carbon tracks (both major causes of misfires).
- Engine oil leaking into the spark plug tubes, from bad valve cover gaskets, is a very common issue on these engines and will eventually lead to cylinder misfires.
- These two cases studies shed more light on how spark plug installation errors and carbon tracks cause misfires:
- Diagnosing A Toyota Corolla Misfire Case Study.
- This real-word case study is a must read on how carbon tracks cause misfires: Carbon Tracks Are A Common Cause Of Ignition Misfires (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
STEP 4: Test the compression of the 'dead' cylinder.
The pistons and cylinder head valves are the ones that draw air into the engine. Usually all cylinders wear out evenly but every now and then, either thru' lack of maintenance or some mechanical problem, you'll have one or more wear out at an accelerated pace.
To make the long story short, those cylinders (with accelerated wear and tear) to produce a less than average compression value that will cause a misfire condition:
- If you've confirmed that the misfiring cylinder is indeed getting spark and its spark plug and spark plug boot are OK, the next step is checking the cylinder's compression.
- The compression test is one of the most overlooked diagnostic tests when it comes to troubleshooting a misfiring cylinder (especially when a P0300 trouble code is involved).
- Compression in the misfiring cylinder should be within 15% of the highest reading among all cylinders. If it's significantly lower, that cylinder will cause a misfire and a cylinder misfire code.
- You can find the engine compression test here:
- This case study digs into how an engine compression issues cause cylinder misfires:
STEP 5: Test the fuel injector of the misfiring cylinder.
- If the 'dead' cylinder has spark and good compression, then the next step is to check its fuel injector.
- On the 1998-1999 models (with a distributor-based ignition system), this is a breeze to do, on the 2000-2007 models, it's a bit more complicated.
- The idea here is to check the injector's internal resistance (with a multimeter) to see if it's suffered an internal open-circuit or a short-circuit issue, causing it to stop spraying fuel.
- Other important checks you'll need to do are:
- Checking the injector connector for damage.
- Checking the wires coming out of the injector connector for dry-rot or peeling insulation.
- Performing a Noid light test on the injector connector to confirm injector activation.
- Checking the injector spray pattern (on the bench) with a DIY injector cleaner kit (like this one here: Universal Fuel Injector Tester and Cleaner Tool Kit (Amazon affiliate link)).
The above list of steps may seem/sound like troubleshooting a misfire is a complicated thing but it really isn't. Depending on your level of 'wrenching' experience, this is something that you can accomplish without taking it to the shop.
What Tools Do I Need To Test The Misfire Code(s)?
Finding the exact cause of the misfire codes or misfire condition is possible with the proper tools. Without them, you won't be able to diagnose/troubleshoot those issues on your 3.0L Honda car or mini-van.
Depending on what the root cause of the misfire is, you may need several tools. Most of these you can buy online, none of these will break the bank and I'll make some recommendations on them. Here's a guide to some of the basic tools that can be and are used:
- Ignition System Tests:
- Spark tester.
- Multimeter.
- 12 Volt test light.
- Fuel System Tests:
- Noid light.
- Fuel pressure gauge.
- Multimeter.
- Engine Mechanical Tests:
- Compression tester.
Now of course, you'll also need basic hand tools like: screw-drivers, ratchet wrenches, sockets, etc. You'll also need a generic scan tool to retrieve the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the computer's memory (if OBD II equipped).
Keep in mind that using the right tool for the job will save you time, frustration, and /or keep you from damaging the component that you're testing.
More 3.0L V6 Honda Accord Tutorials
You'll find a complete list of 3.0L V6 Honda Accord tutorials in the following index:
Here's a small sample of the articles/tutorials you'll find in the index:
- P0108 MAP Sensor Code Explained (1998-2007 3.0L V6 Honda Accord).
- How To Test For A Broken Timing Belt (1998-2007 3.0L V6 Honda Accord).
- How To Troubleshoot A No Start (1998-2007 3.0L V6 Honda Accord).
- MAP Sensor Code Won't Go Away (1998-2007 3.0L V6 Honda Accord).
If this info helped, spread the word!

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!


