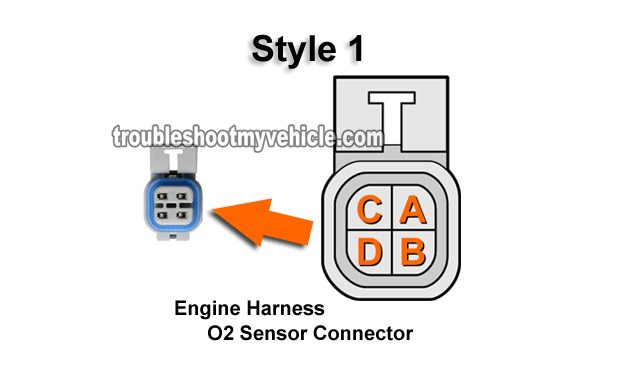
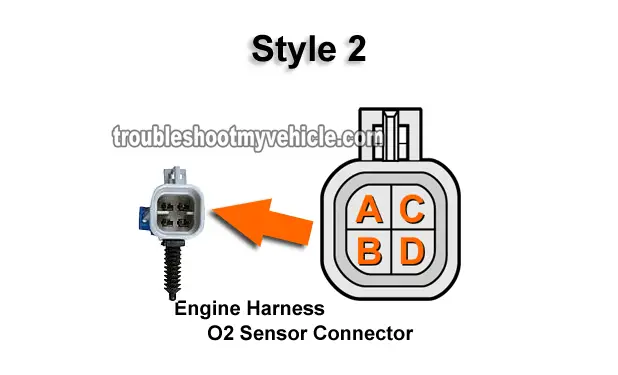
TEST 2: Checking Ground (Circuit C Wire)
The second test (of 3), is to make sure that the PCM is activating the heater element by providing it with Ground.
This Ground is provided by the PCM internally, so you need to be careful NOT to short this wire to power (battery voltage) or you run the risk of frying the PCM (Powertrain Control Module = Fuel Injection Computer).
This is what you'll need to do:
- Disconnect the rear oxygen sensor (if it isn't already from TEST 1).
- Locate the circuit C circuit wire.
- You'll test the wire that is on the engine wiring harness connector side.
- This is usually the Black of the 4 wires.
- Remember: Identify the style of oxygen sensor connector using the illustrations in the image viewer above so that you'll test the correct circuit.
- Place your multimeter in Volts DC mode and:
- Connect the Red Multimeter Lead to Battery Positive (+) Terminal.
- Connect the Black lead to the C circuit wire of the engine wiring harness connector side.
- With the Key On Engine Off, this wire should have 10 to 12 Volts DC.
Let's take a look at your test results:
CASE 1: The multimeter registered 10 to 12 Volts DC. This is good, since this test proves that the PCM is providing the Ground the O2 sensor's heater element needs to activate.
Now that we know that the post-catalytic converter O2 sensor's heater element is getting voltage and Ground, the next step is to test the heater element, inside the O2 sensor, itself. This is a simple resistance done with your multimeter. For this test, go to: TEST 3: O2 Heater Resistance Test.
CASE 2: The multimeter DID NOT register 10 to 12 Volts DC. Re-check all of your connections and make sure you're testing the correct wire.
If your multimeter still does not indicate the 10 to 12 Volts DC, then the D circuit wire has an 'open-circuit' problem somewhere between the O2 sensor connector and the PCM or the PCM is fried (although this is very rare).
Repairing this Ground issue will solve the P0141 and/or P0161 issue you're having with your GM pickup or SUV.
TEST 3: O2 Heater Resistance Test
OK, we're almost done. The very last test (3 of 3), is to see if the heater element inside the Post Catalytic Converter oxygen sensor is fried or not.
So far in your diagnostic, you've checked and confirmed:
- The downstream O2 sensor is being fed with 10 to 12 Volts (TEST 1).
- That it also has a good path to Ground (TEST 2).
OK, this is what you need to do:
- Disconnect the Downstream oxygen sensor from the engine wiring harness connector (if it isn't already from the previous tests).
- NOTE: The O2 sensor must be disconnected from the vehicle's connector for this test!
- Locate the O2 sensor wires that correspond to:
- The circuit C and D.
- Both of these letters should be embossed on the O2 sensor's connector to aid you in further identifying the circuits you need to test.
- Remember: Identify the style of oxygen sensor connector using the illustrations in the image viewer above so that you'll test the correct circuit.
- With your multimeter in Ohms mode, probe the terminals that correspond to the letters C and D of the O2 sensor connector.
- NOTE: Remember, you're testing the oxygen sensor itself.
- If all is OK, you should see about 5 to 16 Ω (Ohms).
- If the heater element is fried, your multimeter will show an open (usually indicated by the letters OL).
Let's take a look at your test results:
CASE 1: The heater element resistance was within specification. This tells you that the heater element within the oxygen sensor is OK.
CASE 2: The heater element resistance WAS NOT within specification (multimeter shows OL). Repeat the test several times to make sure of your test result.
If your multimeter still registers OL, then this test result tells you that you need a new downstream oxygen sensor. Replace the downstream oxygen sensor, this bad boy is fried.
Depending on what downstream oxygen sensor you're testing (either Bank 1 Sensor 2 or Bank 2 Sensor 2), replacing the oxygen sensor will solve the P0141 or P0161 diagnostic trouble code.
Here's why: You have so far:
- Done TEST 1, and you've verified that the post catalytic converter O2 sensor you're testing is getting juice (10 to 12 Volts) with the Key On Engine Off.
- Done TEST 2, and you have confirmed that the PCM is providing a Ground for the O2 sensor's heater element.
- In this test, you have confirmed that the O2 sensor's heater element is fried internally.
So, keeping in mind all of the above, you can replace the O2 sensor with confidence!

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!