
Testing the transmission range switch (known in non-Honda tech speak as the PRNDL switch or park/neutral safety switch) isn't hard.
You don't need any fancy/expensive diagnostic tools to do it since the tests only require a multimeter.
This tutorial will help you check the continuity of the different circuits that make up your Honda's transmission range switch.
Contents of this tutorial:
Symptoms Of A Bad Transmission Range Switch (PRNDL Switch)
It's rare for the transmission range switch to go bad on its own. Most, if not all, of the transmission range switch problems I've diagnosed/repaired have been due human error causing the failure of the switch.
To be a bit more specific: the automatic transaxle (the correct name for a FWD transmission) was removed and the sensor was broken/damaged in the process.
The most common symptoms you'll see when the transmission range switch (PRNDL switch) fails are:
- Your Honda doesn't crank (in other words, the starter motor doesn't activate when you turn the key to start the engine).
- No reverse lights.
- The transmission selections on the instrument cluster (D4, D3, R, N, etc.) don't match the actual gear the transmission is in.
What Does A Transmission Range Switch Do?
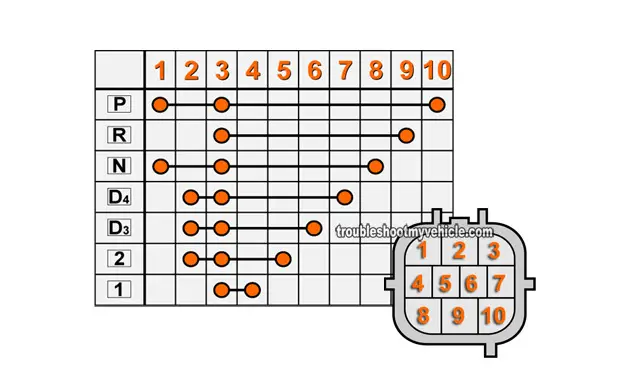
The transmission range switch is part safety device and part PCM sensor (PCM = Powertrain Control Module = Fuel Injection Computer).
The safety device part of the transmission range switch ensures that your Honda cannot be started unless the transmission is in neutral or park and thus prevents the your Honda from moving immediately when it is started.
The sensor part of the switch tells the PCM in what gear the transmission is currently in when you turn the key to the on position or start the engine.
The transmission range switch is know by several names:
- Park/neutral safety switch.
- PRNDL switch.
Alright, let's get testing.
Testing The Transmission Range Switch
Testing the transmission range switch simply involves checking the continuity between certain terminals of the switch with a multimeter.
Using the illustration below, I'll give you an example. Let's say that you want to test the reverse light circuit of the transmission range switch. You would:
- Take the following safety precautions:
- Place chocks behind and in front of the wheels.
- Activate the parking brake.
- NOTE: All continuity tests are done with the Key On Engine Off (KOEO).
- Unplug the transmission range switch from the engine wiring harness' connector.
- Turn the key to the ON position (but don't crank the engine) and place the shift lever in reverse.
- Using the illustration below:
- Check the continuity between the transmission range switch connector's terminal #3 and #9.
- Your multimeter should register continuity.
- Between the transmission range switch connector's terminal #3 and #9.
- Your multimeter SHOULD NOT register continuity between:
- Terminal #3 and any other terminal (that isn't #9).
- Terminal #9 and any other terminal (that isn't #3).
Interpreting the results: If your multimeter registers continuity in the circuits, then the transmission range switch is good. If the multimeter DOES NOT register continuity, then the transmission range switch is bad and needs to be replaced.
Where To Buy The Transmission Range Switch
You could buy the transmission range switch at your local parts store but you'll have to order it and wait to get it.
If you have to wait to get it, why not order the transmission range switch yourself online and save a few bucks in the process?
Click on the link on the left and compare prices and see if it's something worth doing.
I used to buy everything locally, till I found out that buying stuff online is very hassle-free and cheaper. Take a look and compare.
If you're wondering if the transmission range switch fits your particular Honda, don't worry, once you click on the link and get to the site, they'll make sure it fits and if it doesn't, they'll find the right one for you.
More Honda 2.2L, 2.3L Tutorials
You can find a pretty big list of Honda Accord tutorials in this index: Honda 2.2L, 2.3L Index Of Articles.
Here's a small sample of the tutorials you'll find in the index:
- How To Test: TCC Solenoid And Shift Solenoid A (Honda 2.2L, 2.3L).
- How To Test The Radiator Fan Motor (Honda 2.2L, 2.3L).
- How To Avoid A Blown Head Gasket (Honda 2.2L, 2.3L).
- How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (Honda 2.2L, 2.3L).
- How To Test For A Broken Timing Belt (Honda 2.2L, 2.3L).
- How To Test The Igniter, Ignition Coil Accord, Civic, CRV, And Odyssey (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!


