When a fuel injector on your 2.3L Ford Ranger (Mustang or Mazda B2300) fails, its internal resistance changes drastically.
This makes it easy for you and I to test it by simply measuring its internal resistance (and comparing it to what the factory specification is) and I'll show you how in this tutorial.
In case you don't know how to find the bad fuel injector, I'm also going to show you a simple fuel injector diagnostic strategy that will help you find it.
Contents of this tutorial:
ES ![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Los Inyectores De Combustible (2.3L Ford) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar Los Inyectores De Combustible (2.3L Ford) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
CYLINDER MISFIRE DIAGNOSTICS:
Symptoms Of A Bad Fuel Injector
A fuel injector fails in one of several ways. It either:
- Stops injecting fuel completely.
- It doesn't inject enough fuel because its clogged.
- It over injects due to electrical issues.
No matter how the fuel injector fails, the symptoms are pretty much the same ones. These symptoms are:
- Rough idle.
- Lack of power.
- Hesitation when accelerating the vehicle down the road.
- Misfire trouble codes (OBD II equipped only):
- P0300: Random Cylinder Misfire.
- P0301: Cylinder #1 Misfire.
- P0302: Cylinder #2 Misfire.
- P0303: Cylinder #3 Misfire.
- P0304: Cylinder #4 Misfire.
Although this tutorial concentrates on testing a fuel injector that has completely failed, testing a clogged fuel injector isn't that much more complicated and I'll also show you how to diagnose such a condition.
Things To Know Before Testing The Injectors
The one thing that makes testing the fuel injectors on the 1990–1997 2.3L Ford Ranger and 1990-1993 2.3L Mustang a bit involved is that the upper intake manifold plenum has to be removed to reach them.
Now, this isn't a huge job. It can be done without too much hassle. But I want you to keep in mind that a bad or clogged fuel injector isn't all that common on these engines.
Don't get me wrong —a fuel injector doesn't last forever, and it can get clogged. But before you go through the trouble of pulling the plenum, I recommend you first look over this section:
This section will give you a game plan to help narrow down the cause of the cylinder misfire, whether it's really a bad injector or something else entirely.
Following that strategy first could save you the time and frustration of tearing into the intake when the misfire is actually coming from another source.
The Fuel Injector Resistance Test
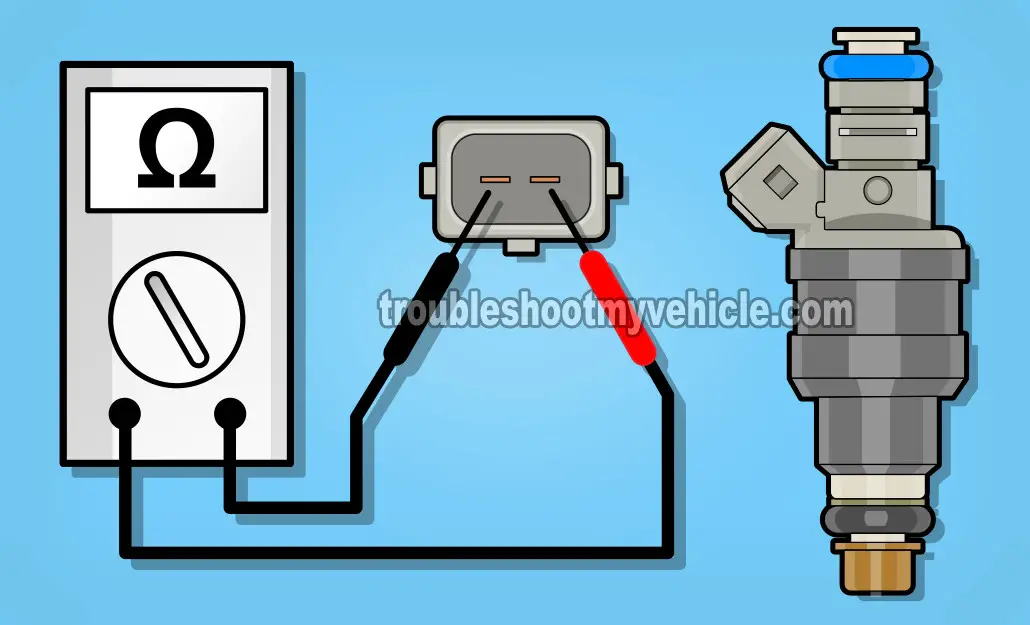
As I mentioned at the beginning of the tutorial, testing a bad fuel injector involves testing its internal resistance.
The internal resistance test checks for a fried fuel injector that has stopped injecting fuel completely and is a very accurate test.
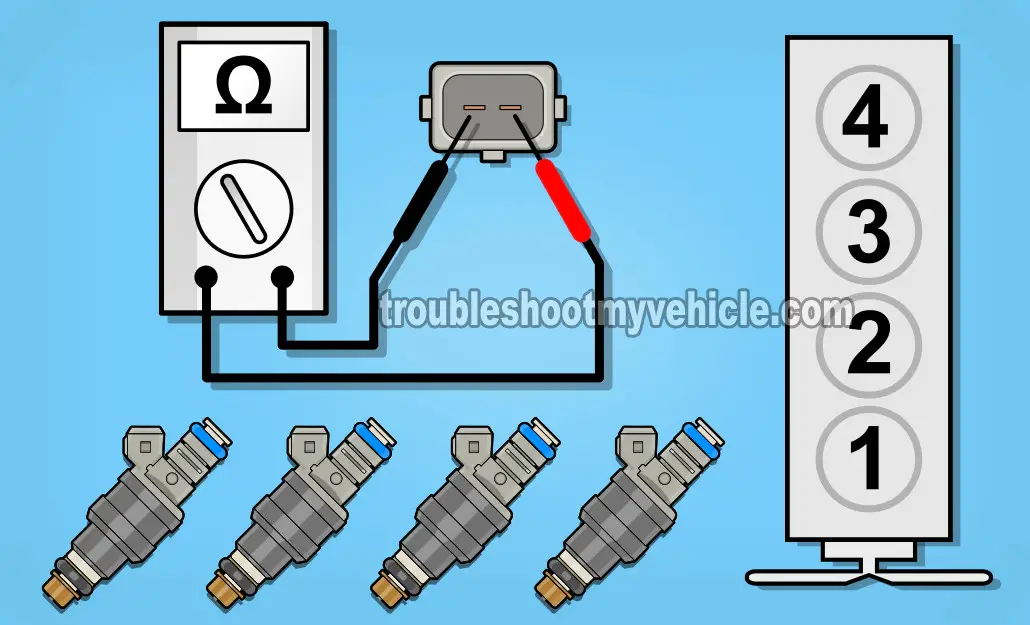
The instructions below assume that you're testing all four fuel injectors on your 2.3L Ford Ranger (Mustang or B2300).
NOTE: To reach the fuel injectors, the intake manifold plenum (upper section of the intake manifold) has to come off. Before starting, review this section: Safety Tips For Removing The Intake Manifold Plenum.
Alright, here are the steps:
- 1
Remove the upper intake manifold plenum.
- 2
Disconnect the fuel injectors from their harness connectors.
You don't have to test them all but I suggest you do. - 3
Set your multimeter to Ohms mode and:
measure the resistance of the fuel injector across its two male spade terminals with the multimeter test leads. - 4
You should see the following resistance:
- 2.3L Ford Ranger
- 1990-1993 fuel injector resistance: 15 to 18 Ωs.
- 1994-1997 fuel injector resistance: 11 to 18 Ωs.
- 2.3L Ford Mustang
- 1990-1991 fuel injector resistance: 15 to 19 Ωs.
- 1992-1993 fuel injector resistance: 13 to 16 Ωs.
- 2.3L Mazda B2300
- 1994 fuel injector resistance: 12 to 16 Ωs.
- 1995-1997 fuel injector resistance: 11 to 18 Ωs.
- 2.3L Ford Ranger
- 5
Repeat steps 1 through 3 on the remaining fuel injectors.
Let's find out what your specific multimeter test results mean:
CASE 1: All fuel injectors registered the same resistance values. This confirms that the fuel injector your are testing is OK.
Here's why: If any one of the fuel injectors were bad, your multimeter would've registered a completely and totally different resistance value (for that fuel injector). Since your resistance (Ohms) Value were the same for all, this is an indication that the fuel injectors do not have an internal electrical fault.
CASE 2: One of the fuel injectors registered a completely different resistance value. This indicates that the fuel injector is bad. Replace the fuel injector.
Safety Tips For Removing The Intake Manifold Plenum
On the 2.3L Ford engine, the fuel injectors sit under the intake manifold plenum. To test or replace them, you'll have to pull the plenum off to get access.
Before you do, there are a few key safety steps to keep in mind so the job goes smoothly and doesn't turn into a bigger headache than it needs to be.
- Keep hardware out of the engine bay: As you remove bolts, nuts, or brackets, put them in a tray or container away from the intake area. The last thing you want is something falling into the intake runners once the plenum is off.
- Cover the intake runners right away: Have clean rags or shop towels handy. As soon as the plenum is removed, stuff the rags into the exposed runners. This keeps any loose metal or debris from dropping inside the engine.
- Always use fresh gaskets: Don't reuse the old plenum gasket. Install new ones every time, and leave them dry —no RTV or sealer. Adding sealer can actually cause a vacuum leak and create more problems down the road.
If something does fall into an intake runner without you noticing, it'll cause serious engine damage as soon as you fire it up. In most cases, the only way to fix that kind of mistake is to pull the cylinder head back off the engine —not a situation you want to be in.
The good news is removing the intake manifold plenum on these engines isn't difficult if you follow these precautions. Keep these basics in mind, and you'll get the job done without complications.
Fuel Injector Diagnostic Strategy
Finding the bad fuel injector or a fuel injector that's clogged (and thus not spraying fuel) is not hard to do, if you have a specific diagnostic strategy. In this section, I'm gonna' share with you my way of diagnosing a fuel injector that will work in any DIY environment.
I first start by:
- Identifying the misfiring (or 'dead' cylinder) first.
- If your Ford Ranger or Mazda B2300 is OBD II equipped, this can easily be done by checking for misfire trouble codes with a scan tool.
- You won't always have a specific bad fuel injector code, but you'll definitely have a misfire code (around 90% of the time that is).
- If no codes are present, then the next best thing to do is a cylinder balance test. This test test is done by simply unplugging one fuel injector at a time, while the engine is running to see if it unplugging it worsens the engines idle.
- If the engine idle DOES NOT get worse, then that cylinder is 'dead' and is the one causing the misfire.
- If the idle DOES get worse, then that cylinder is OK and not the cause of the misfire.
- Check the ignition system for spark.
- After finding the 'dead' cylinder, it's important to make sure that each and every engine cylinder is getting spark.
- This tutorial will help you with that: How To Test The Coil Packs, Ignition Module And CKP Sensor (1989-1994 2.3L Ranger, Mustang, B2300)
- It's important that you check that the spark plug boot and spark plug are NOT soaked (or swimming) in engine oil.
- You should also remove the spark plugs and check them for cracks or carbon tracks (this is SO important).
- Here's a real life case study on carbon tracks and how they can cause a misfire: Carbon Tracks Are A Common Cause Of Ignition Misfires (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- Check engine compression.
- After making sure that the ignition system and all its components are OK, you need to check for low engine compression.
- This is one of the most overlooked tests when diagnosing a misfire or rough idle condition.
- You can find the test here: How To Test The Engine Compression (2.3L Ranger, Mustang, B2300) (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- Noid light test.
- If every test above checks out OK, then the next step is to do a fuel injector Noid light test.
- The Noid light test will help you make sure that the fuel injector is being activated.
- The following Noid light article/tutorial may help you: How To Use A Noid Light And Where To Buy It (at: easyautodiagnostics.com -I know that this is not the most in-depth article on the subject, but it should give you an idea of what is involved..
- Swap the fuel injector with its neighbor on the fuel injector rail.
- If I've found out that I have a specific 'dead' cylinder, I'll swap out the fuel injector if:
- The ignition system is not at fault.
- The cylinder's compression value is good (compared to the rest of the cylinders).
- The fuel injector resistance is good
- I think the fuel injector is clogged.
- If I've found out that I have a specific 'dead' cylinder, I'll swap out the fuel injector if:
The above testing strategy may seem like overkill or too difficult but it isn't. Most of the above tests can be done pretty fast and are not hard to do.
I can tell you from experience that the way to save yourself the frustration of replacing good parts, your vehicle doesn't need and that don't solve the problem, is testing everything. Thankfully, there's a test for just about anything on your car!
Where To Buy The Fuel Injector And Save
The following links will help you to comparison shop for the fuel injector on your 2.3L Ford:
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If my tutorials help you, using these links is an easy way to support the site at no extra cost to you. Thank you!
Not sure if the above fuel injectors fit your particular 2.3L Ford? Don't worry, once you get to the site, they'll make sure it fits. If it doesn't, they'll find you the right one.
More 'How To Test' Tutorials
You can find a pretty big list of 2.3L Ford tutorials in this index: Ford 2.3L Index Of Articles.
Here's a small sample of the tutorials you'll find in the index:
- How To Diagnose A Misfiring Cylinder (2.3L Ford Ranger, Mustang, B2300).
- How To Test The Engine Compression (2.3L Ranger, Mustang, B2300) (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- Test The Ignition Module And Crank Sensor (2.3L Ranger, Mustang, B2300) (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- How To Test For A Blown Head Gasket (2.3L Ranger, Mustang, B2300) (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).
- How To Test The Ford Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor (at: easyautodiagnostics.com).

If this info saved the day, buy me a beer!





