A trouble code P0141: Heated Oxygen Sensor Circuit (Sensor #2) on your 1996-1997 1.6L Toyota Corolla usually means that the post-catalytic converter oxygen sensor's internal heater is fried.
To be sure that the O2 sensor is fried and that it needs to be replaced, you can test it yourself with two basic tests. These two are: making sure the rear O2 sensor's heater is getting power and Ground, and then checking the heater's internal resistance.
The only thing you'll need is a multimeter since you don't need an expensive scan tool to do it!
Contents of this tutorial:
![]() You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Código P0141 (1996-1997 1.6L Toyota Corolla) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
You can find this tutorial in Spanish here: Cómo Probar El Código P0141 (1996-1997 1.6L Toyota Corolla) (at: autotecnico-online.com).
Circuit Descriptions Of The Downstream Oxygen Sensor

The rear O2 sensor heater has two basic jobs: The first is to get the O2 sensor to its operating temperature as fast as possible when you start the engine. This ‘operating temperature’ is usually 600°F +.
The second is that it has to keep the O2 sensor at operating temperature thru' all engine operation conditions (especially engine idle).
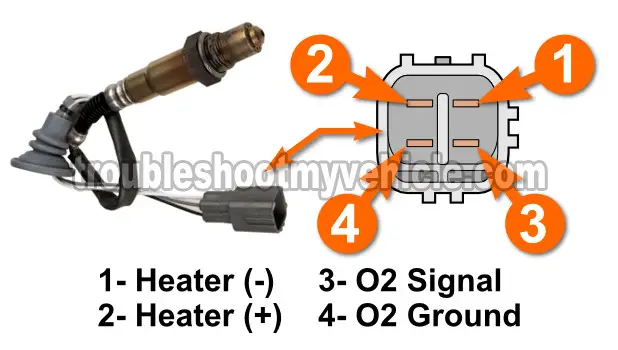
The heater activates when it gets power and Ground. To test it, you and I need to know which 2 of the 4 wires supply them. With this in mind, the table below has the color description of the wires of the rear O2 sensor engine wiring harness connector.
One last thing you need to know: Checking for power and Ground is done on the O2 sensor's engine wiring harness connector. This connector has female terminals. Testing the heater's resistance is done on the O2 sensor's connector itself and this connector has male terminals.
| Downstream Oxygen Sensor (HO2S 12) Pinout (1996-1997 1.6L Toyota Corolla) |
||
|---|---|---|
| Pin | Wire Color | Description |
| 1 | BLU/BLK | Heater Ground (-) |
| 2 | BLK | Heater Power (+) |
| 3 | BLK | O2 Signal |
| 4 | BRN | O2 Signal Ground |
NOTE: I'll be referring to oxygen sensor #2 simply as the rear or downstream oxygen sensor. In case you're wondering, this oxygen sensor is known by several different names:
- Rear Heated Oxygen (O2) Sensor.
- HO2S 1/2.
- Downstream Oxygen (O2) Sensor.
- Oxygen Sensor Bank 1 Sensor 2.
- Post-Catalytic Converter O2 Sensor.
Where To Buy The Oxygen Sensor And Save Some $$$
If the rear oxygen sensor's heater is fried, the following links will help you to comparison shop and save money on a new oxygen sensor.
NOTE: If you're not sure if the above O2 sensor fit your particular 1.6L Toyota Corolla don't worry, once you get to the site, they'll make sure the sensor is the right one, if not, they'll find you the right one.
TEST 1: Verifying The Heater Element Is Getting Power And Ground

We're gonna' start by making sure that the following 2 wires, of the engine wiring harness connector, have power and Ground:
- The black (BLK) wire.
- The blue with black stripe (BLU/BLK) wire has Ground (this Ground is provided by the PCM).
Since the rear O2 sensor's engine wiring harness connector has 2 black wires, you can identify the correct black wire because it connects to the pin labeled with the #2 in the illustration above.
CAUTION: Be careful and test the O2 sensor with a completely cold engine! The O2 sensor and the exhaust pipe it's bolted into gets extremely hot and stays hot long after the engine has been turned off. Be careful and take all necessary safety precautions! Also, don't trust the jack to keep your Corolla up in the air -place it on jack stands!
IMPORTANT: The illustration of the connector above is of the connector on the oxygen sensor itself. To check for power and Ground you'll test the connector of the engine wiring harness sensor (which has female terminals).
OK, this is what you'll need to do:
- 1
Locate the downstream oxygen sensor and disconnect it from its engine wiring harness connector.
- 2
Set your multimeter to Volts DC mode and turn the key ON but don't crank or start the engine (this will power up the O2 sensor's engine wiring harness connector).
- 3
With your multimeter test leads, probe the female terminals that correspond to the black and pink wires of the connector.
Remember, you're testing the engine wiring harness O2 sensor connector (which has female terminals) and not the connector of the O2 sensor itself. - 4
With the Key On Engine Off (KOEO), your multimeter should register 10 to 12 Volts DC.
Let's take a look at your test results:
CASE 1: Your multimeter registered 10 to 12 Volts DC. Good, since this confirms that the rear oxygen sensor's heater element is getting power and Ground.
The next step is to verify that the heater's resistance is within specification. For this test, go to: TEST 2: Testing The Heater Element's Resistance.
CASE 2: Your multimeter DID NOT register 10 to 12 Volts DC. The most likely cause is that power is missing due to a blown fuse or a short (or open) in the wiring. You'll need to check the fuse in the fuse box and make sure it's not blown.
If the fuse is OK, your next step is to find out why this battery power (or ground) is missing using a wiring diagram.




