What Tests Can I Perform To Find The Cause Of The Misfire Condition?
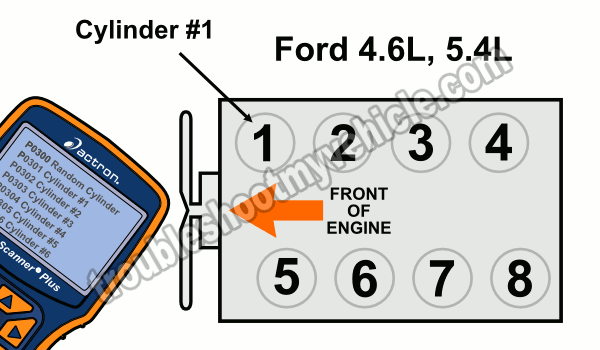
You can pinpoint the exact cause of a misfire on your Ford (or Mercury) 4.6L or 5.4L equipped car (or SUV or pick up) and thankfully, there is a logical starting point for troubleshooting/diagnosing a misfire condition (hopefully this article will be your road map to get it done).
The very first thing that you'll need to do is to find out which engine cylinder is the one that's dead. By dead, I mean not contributing to the overall power the engine produces. Remember, just one dead cylinder (either because the spark plug or fuel injector or coil is bad) will cause the engine to miss (run rough, misfire, etc.).
This is usually accomplished by using a scan tool and reading the codes stored in the PCM (Powertrain Control Module= Fuel Injection Computer). Then, by using an illustration (like the one in the image above) to identify which cylinder is the one affected (Don't have a scan tool? Need a scan tool? Check out my recommendation: Actron CP9580 Scan Tool).
I want to stress the part where I wrote ‘usually accomplished by using a scan tool’ because as important as it is to own and know how to use a scan tool, a misfire condition can be troubleshooted and diagnosed without a scan tool.
Now, before I get too ahead of myself, the key to troubleshooting a misfire condition without a scan tool is by knowing how to do a cylinder balance test but more about this a little later.
The following are my recommendations as to what to start testing first. Although you don't have to follow the list in that particular order:
The following is my recommended misfire troubleshooting/diagnostic strategy:
STEP 1: Connect a scan tool to read any misfire codes or other diagnostic trouble codes. A misfire, unfortunately won't always set a diagnostic trouble code, so it may be necessary to do a cylinder balance test to find out which cylinder or cylinders are misfiring (you can find the cylinder balance test on the last page of this article here: Where Do I Find The Test Articles?).
STEP 2: Since misfires are usually a product of something having gone wrong in the ignition system (specifically a bad COP coil or a bad coil pack), the next step or steps is checking that the misfiring cylinder is getting spark.
STEP 3: Removing and visually checking the spark plug wire (or COP ignition coil and its boot) and spark plug to check for wear and tear, Carbon Tracks, anti-freeze, etc.
STEP 4: If testing the ignition system tells you that the problem is somewhere else, then next steps are checking fuel injectors, compression tests, Vacuum Leaks, etc.
The above list of steps may seem/sound like troubleshooting a misfire is a complicated thing but it really isn't. Depending on your level of ‘wrenching’ experience, this is something that you can accomplish without taking it to the shop (if you have already replaced the spark plugs on your 4.6L or 5.4L engine, this is something you can handle easily).
Also, I have written the articles that will cover most of the tests described above that will help you to diagnose the misfire (you'll find the links to them in the next page in the section: Where Do I Find The Test Articles?).
What Tools Do I Need To Test The Misfire Code(s)?
Finding the exact cause of the misfire codes or misfire condition is possible with the proper tools. Without them, you won't be able to diagnose/troubleshoot those issues on your 4.6L or 5.4L V8 Ford car or pickup.
Depending on what the root cause of the misfire is, you may need several tools. Most of these you can buy online, none of these will break the bank and I'll make some recommendations on them. Here's a guide to some of the basic tools that can be and are used:
- Ignition System Tests:
- Spark tester.
- Multimeter.
- 12 Volt test light.
- Fuel System Tests:
- Noid light.
- Fuel pressure gauge.
- Multimeter.
- Engine Mechanical Tests:
- Compression tester.
Now of course, you'll also need basic hand tools like: screw-drivers, ratchet wrenches, sockets, etc. You'll also need a generic scan tool to retrieve the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the computer's memory (Don't have a scan tool? Need a scan tool? Check out my recommendation: Actron CP9580 Scan Tool).
Keep in mind that using the right tool for the job will save you time, frustration, and /or keep you from damaging the component that you're testing.
